Centralized Management: Definition, Benefits, and Cybersecurity Role


Centralized management in cybersecurity refers to bringing all security tools, policies, and processes under one integrated system or platform. Instead of different departments handling security in isolation, centralization creates a single point of control for the entire infrastructure. This unified approach improves visibility, strengthens oversight, and ensures that security standards are applied consistently across networks, endpoints, cloud environments, and applications.
Key advantages include uniform policy enforcement, quicker detection and response to threats, optimized use of resources, and easier compliance with regulations. By breaking down silos, centralized management offers a complete view of an organization’s security posture and enables more coordinated, effective actions when responding to incidents.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, organizations with fully centralized identity management cut breach lifecycle costs by 28% compared to fragmented systems. This shows why centralized management is essential for both strong cybersecurity and efficient operations. Let’s explore more in this blog.
Key Takeaways:
- Centralized management concentrates decision-making at the top for consistent policies and oversight.
- It ensures efficiency and accountability, but can slow adaptability and limit autonomy.
- Examples include small businesses, Apple’s historic model, and centralized IAM systems.
- Compared to decentralized models, it offers more control but less flexibility.
- In cybersecurity, it boosts visibility, compliance, and risk reduction across systems.
What Is Centralized Management?
Centralized management is the practice of overseeing cybersecurity processes through a single set of tools, procedures, and systems. It removes silos between departments, enabling unified oversight, streamlined compliance, and reduced redundancies. In a centralized management system (CMS), administrators plan, assess, implement, authorize, and monitor all cybersecurity tools across the organization.
Why Centralized Management Is Necessary
Centralized management has become essential for modern organizations because it consolidates security oversight into a single framework. By unifying visibility, documentation, and compliance, it reduces miscommunication and eliminates unnecessary redundancies. At the same time, it lightens the burden on critical infrastructure like firewalls, making security operations more efficient and reliable. Key benefits include:
-
Gain more visibility
Centralized management provides all teams with a unified view of network operations, allowing them to monitor the impact of their work and respond effectively to issues. -
Document network activities
A CMS keeps detailed logs of anomalies and events, supporting root cause analysis, troubleshooting, and improving the overall efficiency and security of the network. -
Ease the burden on firewalls
Managing all security features from a single server reduces firewall workload, increases throughput for safe traffic, and simplifies overall firewall administration. -
Ensure compliance
Centralized management streamlines adherence to compliance standards, controls data access, enforces uniform security policies, and makes audits faster and more efficient.
Key Features of Centralized Management
Centralized management is defined by its focus on authority, control, and uniformity across an organization. It ensures that decisions, processes, and communication are streamlined for efficiency, security, and compliance.
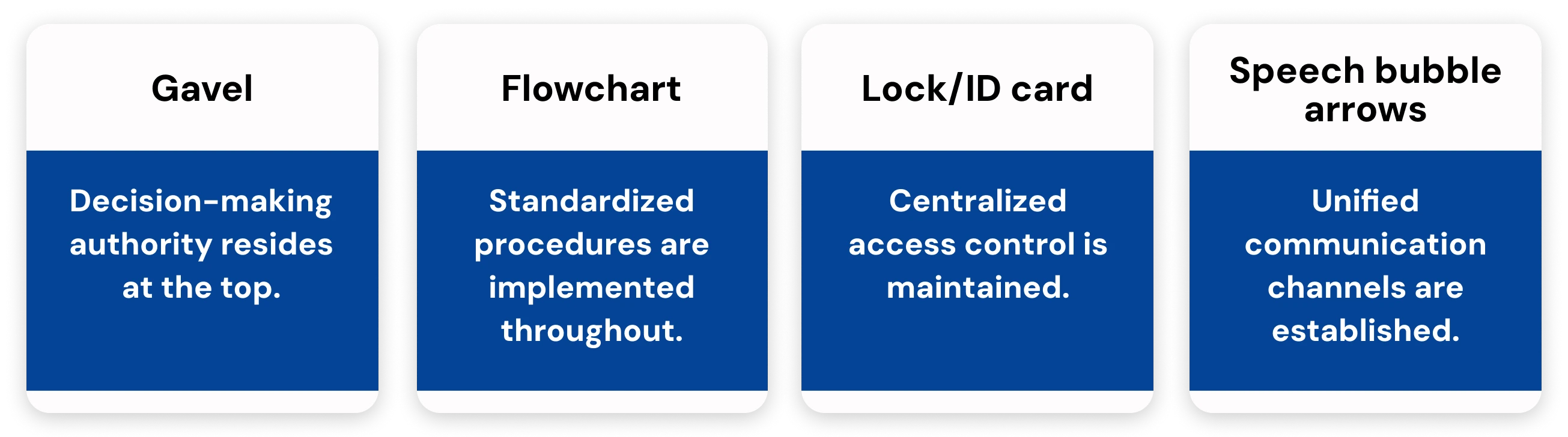
1. Top-down decision-making
All strategic and critical decisions are made by top management, while lower-level managers and employees execute these decisions according to directives. This ensures organizational goals are aligned, responses to issues are swift, and accountability is clear at every level.
2. Standardized procedures across the organization
Policies, processes, and workflows are uniform across departments, locations, and teams. Employees are expected to follow these standardized procedures, and changes or deviations require approval from upper management, reducing operational inconsistencies and security risks.
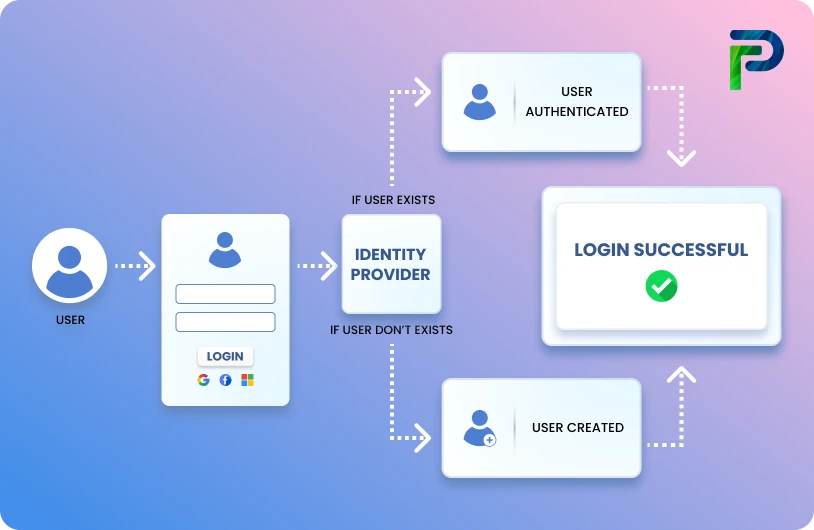
3. Centralized identity & access administration
A core aspect of centralized management is centralized identity and access administration. With this approach, identity management systems, access controls, and user permissions are governed from a central point, ensuring that all users follow strict role-based access policies.
By implementing centralized access control, organizations can prevent unauthorized access, protect sensitive data, and streamline security operations. Centralized security management also simplifies compliance audits, giving teams a clear view of who has access to what and helping maintain regulatory adherence across the enterprise.
4. Unified communication flow
Centralized management also relies on a unified communication flow, where updates, directives, and security protocols are communicated from the executive level down to all teams. This structured top-down approach ensures everyone receives the same information, reducing misunderstandings and supporting consistent policy implementation.
In cybersecurity, this unified flow reinforces centralized security management by keeping employees informed about organizational updates, security guidelines, and compliance requirements. By combining centralized communication with centralized identity management, organizations can maintain a cohesive, secure, and well-informed workforce.
Advantages of Centralized Management
Centralized management provides organizations with structured control, uniformity, and strategic alignment. By consolidating authority and decision-making, it improves efficiency, accountability, and resource optimization across all departments.
1. Consistency in decision-making
With strategic decisions made by top management, the organization ensures uniform policies, goals, and procedures across all departments. This consistency reduces confusion, aligns objectives, and helps employees clearly understand their roles, responsibilities, and expected outcomes.
2. Strong oversight & accountability
Centralized management enables senior leadership to monitor operations, policies, and compliance effectively. By maintaining control over critical processes, management can quickly identify issues, enforce standards, and ensure accountability at every level, improving overall performance and operational quality.
3. Efficient resource allocation
Having a centralized view of organizational needs, objectives, and finances allows leaders to allocate resources strategically. This ensures that personnel, budgets, and technology are deployed where they are most needed, minimizing waste and maximizing operational efficiency.
4. Clear strategic direction
By concentrating authority at the top, centralized management provides a unified vision and clearly defined organizational goals. This ensures that all departments work toward the same objectives, enabling coordinated efforts, faster decision-making, and improved long-term results.
Disadvantages of Centralized Management
While centralized management provides control and consistency, it also comes with challenges that can affect organizational agility, employee engagement, and leadership efficiency. Understanding these drawbacks is important for implementing the system effectively.
1. Slower response times
Centralized decision-making can delay reactions to changing market conditions or urgent operational issues because most decisions require approval from top management. This slower responsiveness can impact customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and the organization’s ability to adapt quickly.
2. Risk of delays
Concentrating critical decisions with a few leaders creates potential slowdowns in workflow and project execution. When approvals or instructions are delayed, productivity can suffer, and teams may be unable to act promptly on important tasks.
3. Limited employee autonomy
Employees in centralized organizations generally have minimal decision-making authority, which can reduce motivation and limit opportunities for innovation. Lack of empowerment may prevent staff from contributing creative solutions or responding independently to local challenges.
4. Overload on leadership
Senior management is responsible for most strategic planning, approvals, and policy enforcement, which can lead to excessive workload and burnout. This strain can reduce leadership effectiveness, slow decision-making, and increase the risk of errors in critical organizational processes.
Examples of Centralized Management in Action
Centralized management is implemented across various organizations and industries, ensuring consistent decision-making, streamlined operations, and strong oversight. Here are some illustrative examples:
1. Small businesses (owner-led decisions)
In many small businesses, the owner or founder retains full control over strategic and operational decisions. This centralized approach ensures that policies, procedures, and business strategies are consistently applied, enabling quick alignment across staffing, service delivery, and customer experience while maintaining accountability.
2. Tech companies (Apple’s historic model)
Apple has historically operated with a centralized management structure, where all major product, design, and strategic decisions are made by top leadership at the headquarters. This model guarantees uniform quality standards, cohesive product development, and consistent global implementation of business strategies, maintaining brand integrity and operational efficiency.
3. Cybersecurity: centralized identity & access management systems
Global enterprises often deploy centralized identity and access management (IAM) systems to handle thousands of employees, contractors, and partners across multiple regions. From a single hub, IT teams can assign user permissions, enforce authentication, and monitor activity consistently across all platforms. For instance, financial institutions use IAM to meet strict compliance requirements, reduce insider threats, and quickly revoke access when employees leave. This demonstrates how centralized management strengthens both security and operational control.
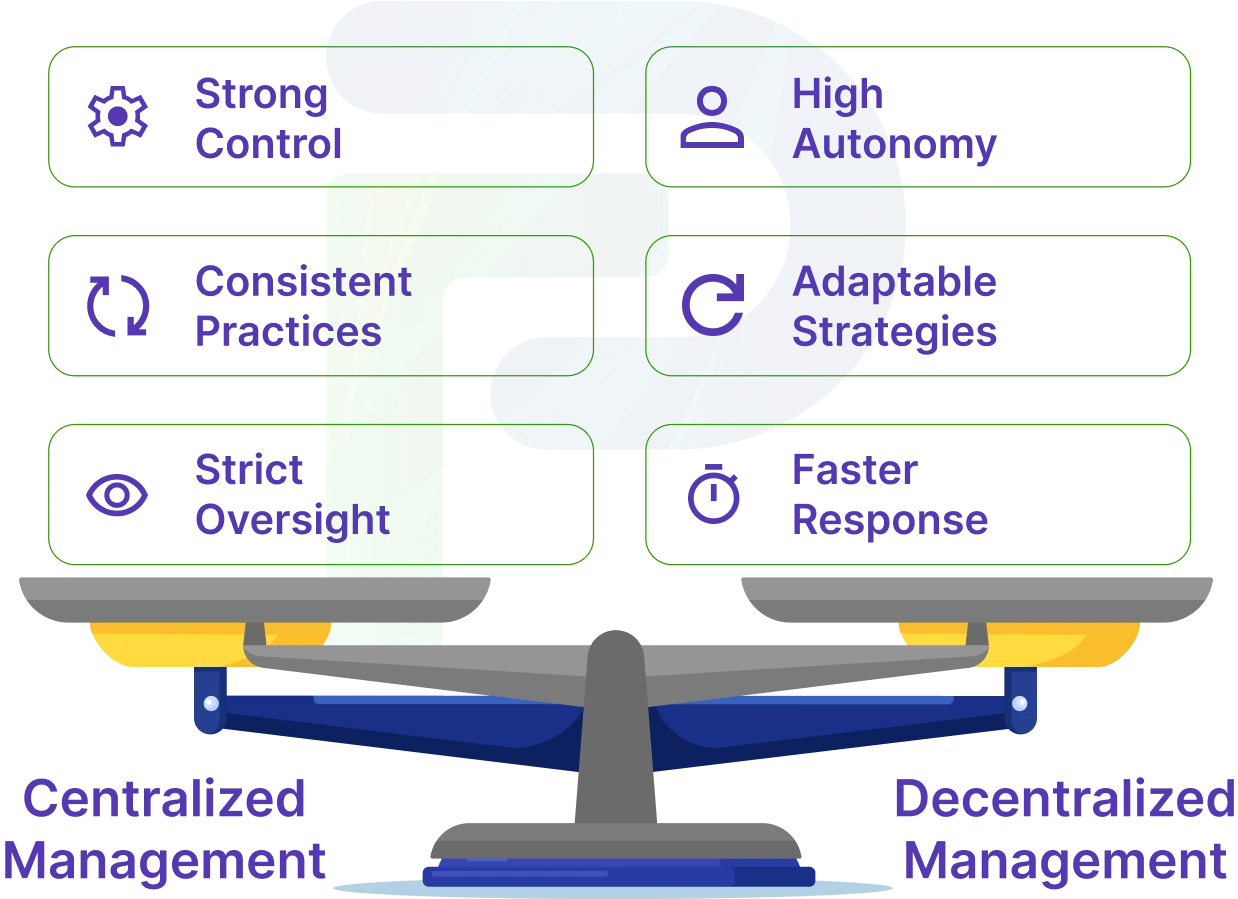
Centralized vs. Decentralized Management
Centralized and decentralized management differ in decision-making, authority distribution, and team operations. Knowing their differences helps choose the structure best suited for an organization’s goals and size.
| Sr No | Feature | Centralized Management | Decentralized Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Decision Authority | Authority and strategic decisions are concentrated at the top leadership levels, ensuring consistency and control. | Decision-making is distributed across departments and managerial levels, allowing teams to act independently. |
| 2 | Decision Speed | Decisions may take longer due to multiple layers of approval and top-level oversight. | Decisions are typically faster as local managers or teams can respond immediately without waiting for top-level approval. |
| 3 | Organizational Flexibility | Limited flexibility since most decisions must be approved by senior leadership, reducing adaptability. | Highly flexible as decision-making occurs at multiple levels, enabling quicker adjustments to changing circumstances. |
| 4 | Responsibility & Accountability | Transparent accountability, as a few leaders are responsible for key organizational decisions. | Accountability can be more diffuse because decision-making authority is spread across various managers and departments. |
| 5 | Employee Empowerment | Employees have limited authority and decision-making power, following directives from higher management. | Employees enjoy greater autonomy, making decisions and taking action based on their expertise, role, and seniority. |
| 6 | Ideal Organization Size | Best suited for small to medium-sized organizations where top management can maintain control and oversight. | Works well in larger organizations that need agility and local decision-making to respond quickly to changes and operational needs. |
Cybersecurity & Centralized Security Management
Centralized management plays a critical role in cybersecurity by unifying control over security tools, access, and policies. By consolidating monitoring and administration into centralized consoles, organizations can streamline operations, strengthen security posture, and maintain compliance across the enterprise.
Role in Cybersecurity
Centralized security management relies on unified consoles that integrate firewalls, Identity & Access Management (IAM) systems, and Identity Governance & Administration (IGA) platforms. This approach enables administrators to plan, implement, and monitor all security controls from a single interface, reducing the risk of misconfigurations and improving response times to security incidents.
Benefits
Centralized security management improves how organizations monitor, enforce, and respond to cybersecurity challenges, offering advantages such as:
- Enhanced visibility: A centralized security framework provides a unified view across the entire network, including endpoints and user activities. This visibility enables security teams to detect anomalies, identify potential threats early, and consistently monitor compliance across all systems.
- Regulatory compliance: By consolidating security controls into a single console, organizations can more easily comply with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Centralized management supports unified policy enforcement, maintains comprehensive audit trails, and simplifies the generation of compliance reports.
- Reduced complexity: Centralized management brings together critical security functions such as firewalls, Identity and Access Management (IAM), and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) into one cohesive framework. This reduces tool redundancy, streamlines operational processes, and accelerates incident response.
When Should Organizations Use Centralized Management?
Centralized management is most useful when an organization needs strong oversight, consistent policies, and secure control across all operations. It helps reduce risk and ensures compliance without relying on scattered decision-making.
Where centralized management fits best:
-
Regulated industries: Sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government must follow strict compliance rules. A centralized model makes it easier to enforce the same policies everywhere and stay audit-ready.
-
Scaling cybersecurity programs: As companies grow, having multiple disconnected systems can create security gaps. Centralized management works with IAM and IGA tools to standardize access, improve visibility, and reduce complexity.
-
Organizations handling sensitive data: Businesses in areas like banking, insurance, and defense deal with highly confidential information. Centralized control allows faster incident response and tighter protection of critical assets.
-
Global and distributed teams: Companies with offices or employees in different locations often face inconsistent local practices. Centralization ensures a single framework for access, communication, and compliance across all regions.
Final Thoughts
Centralized management is a strategic approach that drives consistency, efficiency, and strong oversight across the organization. By concentrating decision-making at the top, businesses can align processes, streamline resources, and maintain control. While it may limit flexibility, it’s ideal for industries where compliance, accountability, and security matter most.
In cybersecurity, centralized management strengthens identity and access governance, ensures consistent policy enforcement, and reduces risk. Tech Prescient, helps businesses leverage these frameworks with expert guidance and automation-driven solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is centralized management?
Centralized management is a system where decision-making authority rests at the top level of an organization. This structure ensures consistent policies, clear oversight, and alignment across all teams. It’s ideal for businesses that value control and uniformity.2. What are the benefits of centralized management?
Centralized management provides consistent policies, stronger oversight, and clear strategic direction. It also helps allocate resources efficiently and maintain alignment across departments. Overall, it brings structure and predictability to organizational operations.3. What are the disadvantages of centralized management?
While it strengthens control, centralized management can slow adaptability and create potential bottlenecks. It may also limit employee autonomy and overburden leadership with decision-making. These trade-offs need to be considered for fast-moving environments.4. How does centralized management apply to cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity, centralized management allows all security controls, policies, and identity access to be handled from one console. This approach strengthens governance, reduces risk, and ensures compliance across systems. It makes managing complex security environments simpler and more effective.5. What is the difference between centralized and decentralized management?
Centralized management keeps authority at the top, while decentralized management spreads decision-making across multiple levels. Centralization prioritizes control and consistency, whereas decentralization favors flexibility and faster responses. Both have unique advantages depending on business needs.