
Identity Management Landscape in 2025: Key Trends & Challenges

The Identity and Access Management (IAM) landscape has expanded rapidly over the last decade. It’s no longer limited to employees logging into enterprise systems; today, identities span across partners, customers, and even devices that interact through cloud platforms, mobile applications, e-commerce portals, and social networks. Each of these ecosystems introduces its own identity standards, tokens, and technologies, many of which were never designed to integrate smoothly with traditional enterprise IAM.
The result is a fragmented authentication and authorization environment. Users are often burdened with multiple sets of credentials across different platforms, while organizations struggle to enforce consistent access policies. Without a universal framework to unify these diverse contexts, gaps in visibility, control, and security become inevitable.
Growing cyberthreats, more compliance regulations, and the intricacy of today's IT configurations have all contributed to this shift. The Identity management landscape has evolved into the core of any organization's security policy, no longer being only in the background. It helps businesses ensure that individuals only have access to what they actually require, maintains a clear record of who has what authority, and yet facilitates user login. That the IAM landscape is expanding quickly is therefore not surprising; it is expected to increase by around 13% annually and reach USD 24 billion by 2025, according to Identity Management Institute.
Given that IAM is at the core of digital trust and security, knowing how it has changed over time helps prepare for what comes next. The main themes influencing the identity management market in 2025, the difficulties businesses face, and how IAM is reinventing cybersecurity will all be covered in this article.
Key Takeaways:
- Discover why identity is the new security perimeter in modern cybersecurity
- Understand the growing role and challenges of machine and non-human identities
- Explore how Zero Trust and ABAC are transforming access management
- Uncover the key governance, compliance, and visibility challenges in IAM
- See what the future holds for IAM with AI-driven detection, passwordless tech, and cloud-native solutions
What Is the Identity Management Landscape?
The Identity management (IAM) landscape represents the evolving ecosystem of tools, policies, and technologies that secure digital identities in modern organizations. At its core, IAM focuses on the operational side of granting, modifying, and revoking access to enterprise resources, ensuring that only the right people and systems get the right access at the right time.
Think of IAM as the gatekeeper of the digital enterprise. It manages the full user lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding, while providing efficiency and security at every step. To achieve this, IAM platforms rely on mechanisms such as single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), which not only streamline access but also strengthen protection against identity-based threats.
Key functions of IAM include:
- Ensuring the right people & systems get the right access
IAM enforces role-based and attribute-based access controls to match permissions with business needs. By validating both human and non-human identities, it ensures only legitimate entities gain entry. This reduces the risk of privilege misuse and strengthens the security perimeter. - Authentication and authorization
Authentication confirms a user’s identity using credentials or adaptive methods like MFA and biometrics. Authorization then defines the level of access granted, based on policies and contextual risk. Together, they form the backbone of identity-first security by preventing unauthorized activity. - Lifecycle management of users and identities
IAM automates identity provisioning, modification, and de-provisioning as users join, move, or leave. It ensures that access rights remain aligned with role changes across hybrid and multi-cloud systems. This minimizes orphaned accounts, strengthens compliance, and improves operational efficiency. - Governance to maintain compliance and oversight
IAM governance provides visibility into who has access, why they have it, and how it is used. It enables periodic access reviews, segregation-of-duties enforcement, and regulatory reporting. With strong governance, organizations close oversight gaps and stay compliant with evolving mandates. - Audit
Beyond access control, IAM also plays a key role in tracking and analyzing user behavior. Continuous logging and monitoring help detect unusual or unauthorized activity early, support faster incident response, and provide the audit trails required for regulatory compliance.
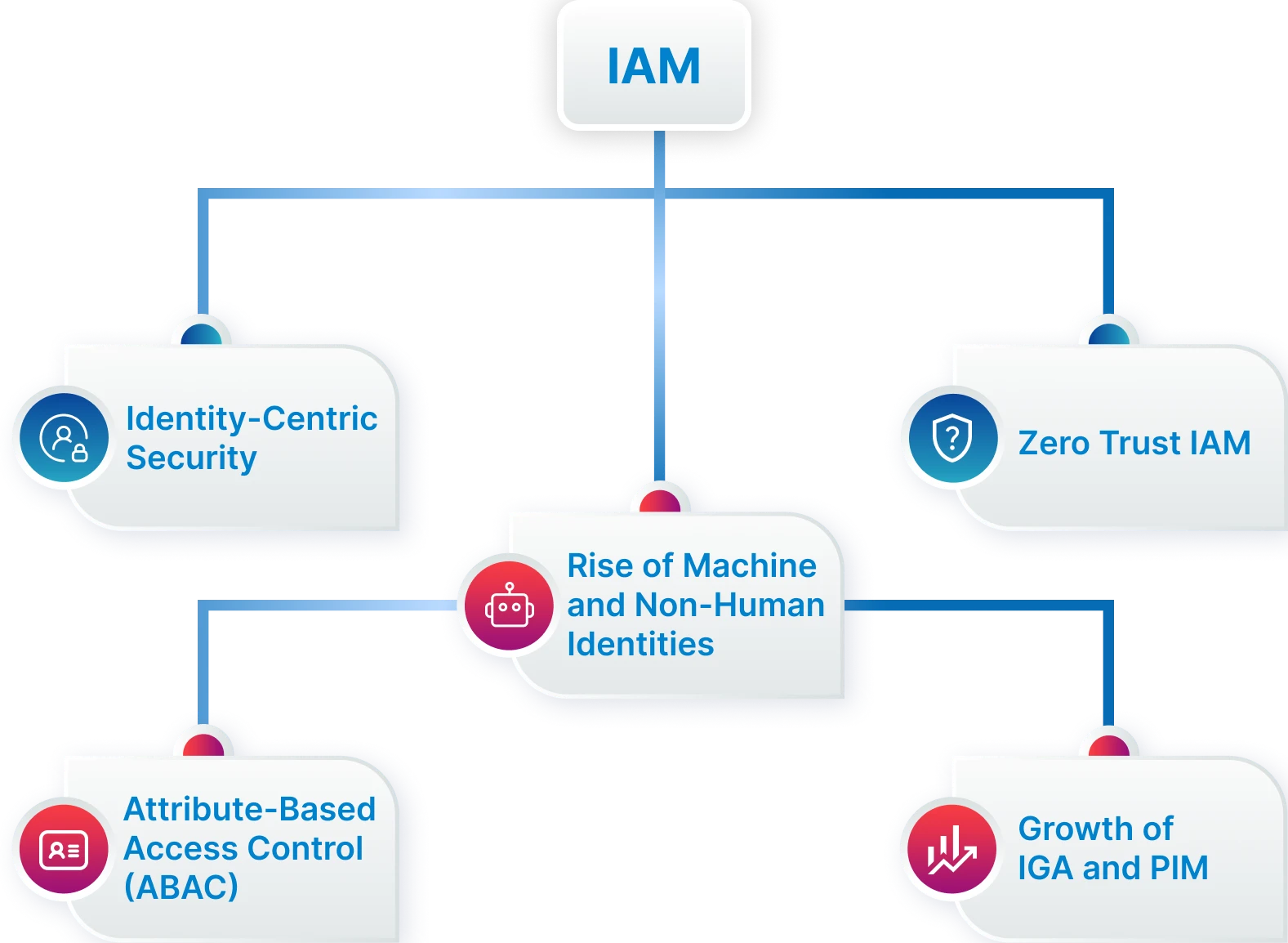
Key Trends Shaping the IAM Landscape
As enterprises accelerate digital transformation, identity is no longer just a security function; it’s the foundation of trust across people, devices, and applications. Emerging trends are reshaping how organizations approach identity, access, and governance in a hyper-connected world. Below are the key shifts defining the future of IAM trends in 2025 and beyond.
Identity-Centric Security
Identity-centric security places the user’s identity, not the network perimeter, at the center of access control. Instead of assuming that everything inside a firewall is trustworthy, this model verifies every user, device, and application before granting access.
As organizations adopt cloud-first strategies and enable hybrid or remote workforces, identity has become the most reliable control point. By treating identity as the new perimeter, enterprises can apply consistent policies across on-premises and cloud systems, ensuring security regardless of where users or resources are located.
This shift reduces the risk of credential theft, insider misuse, and lateral movement by tying access directly to who the user is, what they need, and the context of the request. In practice, identity-centric security strengthens defenses while enabling secure, seamless access to sensitive resources in today’s distributed IT environments.
Rise of Machine & Non-Human Identities
The explosion of digital identities in 2025 is being driven less by humans and more by machines. Service accounts, IoT devices, and AI models now operate at a scale that far outpaces traditional IAM systems, creating a new frontier of risk. Treating these identities with the same rigor as human ones is critical for resilience.
- Service Accounts: These are the invisible backbone of enterprise operations, enabling applications and services to talk to each other. However, they often run with persistent, high-level privileges and lack proper rotation policies. If compromised, they can provide attackers with long-term, stealthy access to critical systems.
- IoT Devices: From smart sensors and cameras to connected medical and industrial devices, IoT endpoints are multiplying across networks. Each one represents a potential entry point if left unverified. Assigning unique digital identities and enforcing secure onboarding ensures these devices don’t become unmanaged “shadow identities.”
- AI Models & Bots: Modern enterprises increasingly rely on autonomous bots, ML pipelines, and AI-driven workloads to handle sensitive tasks. These entities interact continuously with data and infrastructure, demanding automated certificate management, ongoing secret rotation, and strict access boundaries to prevent misuse.
Zero Trust IAM
Traditional perimeter-based defenses are no longer sufficient in a world of hybrid work, cloud-native apps, and evolving threats. Zero Trust Identity and Access Management (IAM) flips the model, assuming no user, device, or session is automatically trusted. Instead, every access request is verified in real time, guided by context such as user behavior, device health, and location.
Zero Trust IAM not only minimizes the risk of unauthorized access but also ensures that users are granted the least privilege necessary to perform their tasks. By combining continuous authentication with adaptive, policy-driven access controls, organizations can safeguard sensitive data against credential misuse and lateral movement within networks.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
As digital environments grow more distributed and complex, traditional Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is showing its limitations. Static roles cannot keep pace with the dynamic requirements of multi-cloud ecosystems, hybrid workforces, and evolving compliance mandates. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) has emerged as a scalable, context-aware alternative that aligns closely with Zero Trust principles.
Unlike RBAC, which assigns permissions strictly based on predefined roles, ABAC evaluates a combination of attributes, such as user identity, device posture, location, time, or even transaction type, to make access decisions. This granular, policy-driven model reduces the risk of “role explosion” and enables organizations to implement fine-tuned security without adding administrative overhead.
By adopting ABAC, enterprises can move toward a more adaptive and future-ready IAM framework. It empowers security teams to enforce least-privilege access dynamically, ensuring that permissions shift as real-world contexts change, rather than relying on rigid role hierarchies.
Growth of IGA & PIM
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) and Privileged Identity Management (PIM) are becoming indispensable pillars of modern IAM strategies. Their rapid growth is fueled by rising compliance demands, sophisticated cyberattacks, and the operational complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Together, they deliver the oversight and control enterprises need to strike the balance between agility and security.
Growth Drivers for IGA
- Regulatory pressure and compliance: With global data privacy laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA tightening enforcement, organizations need IGA to perform audits, manage access certifications, and maintain segregation of duties.
- Foundation for Zero Trust: IGA supports continuous verification and ensures that access rights remain aligned with dynamic user roles and business needs.
- Cloud-driven identity sprawl: The surge in SaaS and cloud adoption has multiplied accounts and entitlements. IGA helps centralize visibility and automate lifecycle processes such as provisioning and deprovisioning, reducing manual overhead.
Growth Drivers for PIM
- Protecting high-value accounts: Privileged accounts, such as system admins or DevOps engineers, are prime targets for attackers. PIM solutions enforce monitoring, session recording, and real-time alerts to secure them.
- Enforcing least privilege: PIM removes always-on administrative access and enables just-in-time provisioning, ensuring privileged rights are granted only when required.
- Adapting to cloud and DevOps: With cloud consoles, APIs, and automation pipelines creating new privileged credentials, PIM extends its reach to safeguard critical infrastructure.
- AI-powered detection: Modern PIM solutions are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance security. These tools analyze user activity patterns and flag anomalous behavior that may indicate compromised privileged accounts. By automating access reviews and correlating activity across systems, AI reduces manual effort while improving accuracy. At scale, this enables faster detection of threats, proactive risk mitigation, and stronger overall protection for critical systems.
Challenges in the IAM Landscape
As organizations embrace cloud adoption, IoT expansion, and AI-driven automation, their identity environments are becoming more fragmented and complex. This introduces significant gaps in visibility, governance, and security, making it harder to manage both human and non-human identities effectively.
Key Challenges:
-
Increased attack surface from cloud & IoT
The shift to hybrid and multi-cloud environments, coupled with the explosion of IoT devices, has drastically expanded the attack surface. Each new endpoint, workload, or service account represents a potential entry point for attackers. Managing identity across these distributed environments adds another layer of difficulty, as enterprises must coordinate between on-premises infrastructure and diverse cloud platforms that often follow different standards and policies.
To make matters more challenging, many organizations still depend on legacy systems that were never designed to integrate with modern IAM frameworks. These outdated environments create visibility gaps, weaken policy enforcement, and complicate the adoption of advanced security measures. Without unified oversight, enterprises risk leaving both human and non-human identities unmonitored and exposed to exploitation. -
Fragmented vendor ecosystem
Most organizations end up using a patchwork of IAM, IGA, and PAM tools from different vendors to meet their diverse security needs. While each solution addresses a specific problem, these tools often don’t integrate well with one another. The result is a fragmented setup where identity data and access policies sit in separate silos, making it difficult to get a unified view of who has access to what.
This lack of coordination creates operational blind spots and forces security teams to rely on manual processes to bridge the gaps. Inconsistent policies, duplicate capabilities, and limited interoperability not only increase administrative overhead but also weaken the overall security posture of the organization. -
Struggles managing machine identities
Non-human identities such as service accounts, IoT devices, APIs, and AI models now outnumber human users. Managing their keys, secrets, and certificates at scale is a daunting task. If not rotated or monitored properly, these machine credentials can become prime targets for attackers seeking persistent access. -
Data privacy & compliance hurdles With global regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA tightening enforcement, compliance is no longer optional. Enterprises must demonstrate strict control over who has access to sensitive data, when, and why. Inconsistent governance across cloud and on-premises systems makes passing audits and avoiding penalties a constant challenge.

IAM vs IGA in the Modern Landscape
In cybersecurity, Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) are often confused because both deal with managing digital identities. The overlap lies in the fact that both ensure users can access systems securely, but their responsibilities differ. IAM (Identity and Access Management) focuses on the operational side, granting, managing, and enforcing access to digital resources. In contrast, IGA (Identity Governance and Administration) emphasizes the strategic layer of governance, compliance, and oversight. While IAM ensures that users can open the “door” to the systems they need, IGA makes sure that only the right people have those keys, can justify why they need them, and that their access complies with organizational policies and regulations.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM provides the operational framework for secure and efficient access across an organization’s systems, applications, and data.
- Authentication and Authorization: IAM ensures every user or system is verified before gaining entry, and once inside, is restricted to only the resources necessary for their role.
- Provisioning: It manages the full identity lifecycle, from onboarding new users, adjusting permissions when roles change, to deprovisioning when someone leaves, ensuring access is always up to date.
- Operational security: It incorporates practices like multifactor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and automated provisioning to reduce risk while keeping workflows smooth.
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA)
IGA builds on IAM by governing how access is managed over time and ensuring it aligns with business rules and regulatory requirements.
- Governance and Oversight: IGA provides visibility into entitlements, enforces policies such as separation of duties, and prevents privilege creep as employees move across roles or projects.
- Access Reviews and Compliance: It facilitates periodic certifications of user rights, ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX, and delivers detailed reporting to make access decisions auditable.
- Compliance assurance: Beyond reviews, IGA strengthens accountability through analytics and dashboards that continuously monitor whether access aligns with organizational policies.
Why Both Are Essential
Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) complement each other and are both critical in a modern security framework. IAM provides the operational backbone by determining who gets access to digital resources and what actions they can perform. IGA builds on top of that foundation with governance, policy enforcement, auditing, and compliance to ensure that access is not only granted but also appropriate, justified, and continuously monitored.
In simple terms, IAM answers the question of “who can get in and what can they do,” while IGA addresses “should they have that access, and is it being managed correctly?” When combined, IAM and IGA deliver a complete ecosystem for secure, compliant, and efficient identity management, an essential requirement in today’s Zero Trust and identity-first security environment.
The Future of the IAM Landscape
As digital ecosystems expand and threats grow more sophisticated, the IAM landscape is evolving rapidly. The future will be defined by intelligence-driven security, seamless user experiences, and architectures designed for cloud-first enterprises.
- AI-Driven Identity Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence is transforming how identity threats are detected and prevented. By analyzing behavioral patterns and access anomalies in real time, AI can flag suspicious activity long before it becomes a breach. This proactive layer adds speed and precision that traditional rule-based systems can’t match. - Continuous, Context-Based Authentication
Static logins are giving way to continuous and adaptive authentication models. Instead of relying on a one-time credential check, systems evaluate contextual factors like device health, location, and user behavior to ensure trust throughout the session. This helps reduce insider threats and account takeovers. - Passwordless Adoption Accelerating Passwords are fast becoming obsolete due to their vulnerability to phishing, credential stuffing, and poor user hygiene. Passwordless methods, such as biometrics, security keys, and mobile authenticators, are gaining traction, offering both stronger security and frictionless user experiences.
- Cloud-Native Identity Stacks (CIEM, ISPM) As enterprises migrate to multi-cloud and hybrid environments, cloud-native identity solutions are taking center stage. Tools like Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) and Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) provide visibility and control across complex cloud setups, reducing misconfigurations and shadow access risks.
Final Thoughts
Identity and Access Management is no longer just an IT function; it’s a critical pillar of modern cybersecurity strategy. In a world where digital identities drive access, collaboration, and innovation, effective IAM is the foundation for security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
At Tech Prescient, we simplify IAM by combining advanced tools, governance frameworks, and AI-driven insights. From secure provisioning and access reviews to Zero Trust enforcement and machine identity management, we ensure your organization controls who accesses what, without slowing down business growth.
Don’t wait until a breach or compliance gap catches you off guard. Secure your systems, data, and users now with a modern IAM strategy from Tech Prescient today and stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the 4 pillars of IAM?
The four pillars of IAM are Authentication, Authorization, User Management, and Governance. Authentication ensures users are who they claim to be. Authorization controls what they can access. User Management and Governance keep identities organized, secure, and compliant.2. What is the concept of identity management?
Identity management is all about ensuring secure and compliant digital access across systems. It makes sure the right people or systems get the right access at the right time. This helps prevent breaches while maintaining business efficiency. At its core, it balances security with usability.3. What are the 4 A’s of IAM?
The 4 A’s of IAM are Authentication, Authorization, Administration, and Audit. Authentication and Authorization verify identity and access. Administration handles user lifecycle and policies. Audit ensures everything is tracked, monitored, and compliant.4. What are the three core elements of identity management?
Identity management revolves around three key elements: Identify, Authenticate, and Authorize. First, you identify the user or system. Then you authenticate to confirm they are legitimate. Finally, you authorize them to access only what they are allowed to.5. How does Zero Trust change the IAM landscape?
Zero Trust shifts IAM from perimeter-based security to continuous verification and least privilege. It assumes no user or system is automatically trusted. Access is granted dynamically based on context, device, and behavior. This reduces risk and strengthens overall security posture.