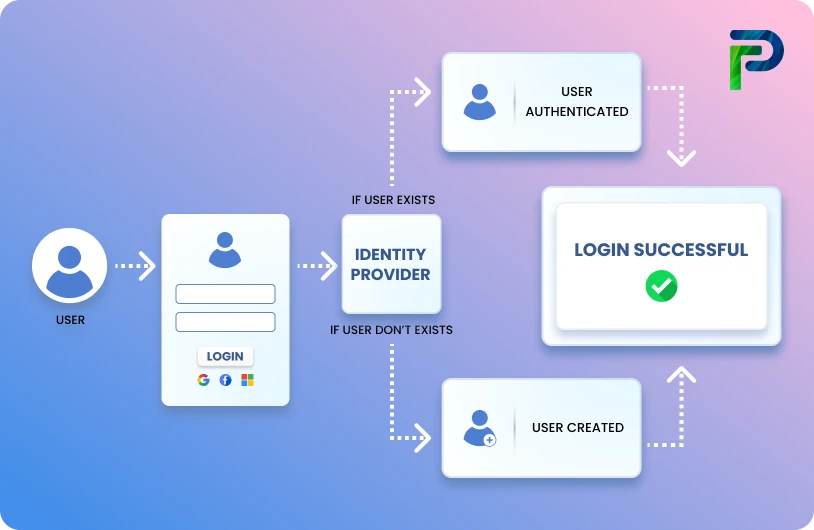
Top 9 IAM Metrics for Secure Access in 2026


Identity and access management (IAM) metrics are key indicators of how successfully your identity programs protect your digital perimeter and enforce secure access. These indicators, which include user access reviews, orphan account discovery, privileged account usage, and MFA adoption, provide IT managers with visibility into risk and opportunity. Measuring these regions allows you to discover misconfigurations, impose the principle of least privilege, and increase IAM maturity.
Many organizations today operate in a hybrid IT environment that spans both on-premises and cloud-based applications. This makes it challenging to maintain a clear, transparent view of who has access to which systems and applications and why. As more workloads continue shifting to digital services, the need for a robust identity management approach becomes critical. Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) has emerged as a key pillar of modern IT security, enabling organizations to establish processes for controlling, managing, and auditing access to data, which is an essential step toward minimizing security risks.
According to the 2025 Ponemon-Sullivan Privacy Report, only 20 percent of organizations say they have fully adopted Zero Trust, and only 24 percent have fully implemented passwordless authentication, showing that many are still catching up in key IAM practices. In this blog, we’ll walk through the IAM metrics that truly matter, why they’re important, and how they can help you strike the right balance between security, compliance, and productivity.
Key Takeaways:
- Learn what identity and access management metrics are and why they’re crucial for security and compliance
- Discover the top 9 IAM metrics every organization should track in 2025
- Understand the benefits and challenges of measuring IAM performance
- Explore best practices and dashboards to improve and monitor IAM metrics
- See real-world use cases and future trends shaping IAM metrics with AI and Zero Trust
What are Identity and Access Management (IAM) Metrics?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) metrics are quantifiable indicators that measure how well an organization’s IAM system performs in terms of efficiency, security, and governance. These metrics track how users are authenticated, authorized, and managed, giving businesses the clarity to spot weaknesses, improve processes, and stay compliant with regulations.
By monitoring IAM metrics, organizations can validate whether their identity governance framework is meeting its objectives. For example, a rising authorization failure rate may indicate that access controls are too restrictive, while a consistently high authentication success rate shows that the login process is smooth and user-friendly.
Tracking IAM metrics provides visibility into:
- The overall security posture of the IAM infrastructure
- The speed and accuracy of onboarding and offboarding users
- Compliance alignment with regulatory requirements
- The ability to detect and respond to insider and external threats
Organizations that consistently track and analyze their IAM metrics, especially when following Gartner’s IAM metrics best practices, are better equipped to identify risks early, prevent breaches, and maintain a seamless user experience.
Why IAM Metrics Are Important
Implementing Identity and Access Management (IAM) metrics delivers measurable advantages across security, compliance, operations, and cost control. By tracking and analyzing these indicators, organizations gain the visibility needed to strengthen governance and continuously improve their identity programs.
- Reducing insider threats:
IAM metrics provide visibility into user access patterns and privilege escalations, helping security teams detect anomalies that may indicate insider misuse. Continuous tracking ensures that users retain only the access necessary for their roles, limiting opportunities for abuse. - Improving operational efficiency:
Metrics that measure provisioning, deprovisioning, and access approval times streamline the onboarding and offboarding process. Faster and more accurate adjustments reduce administrative overhead while ensuring employees and contractors have the right level of access at the right time.
In short, IAM metrics are essential for creating a secure, compliant, and efficient identity environment while driving continuous improvement and supporting business resilience.
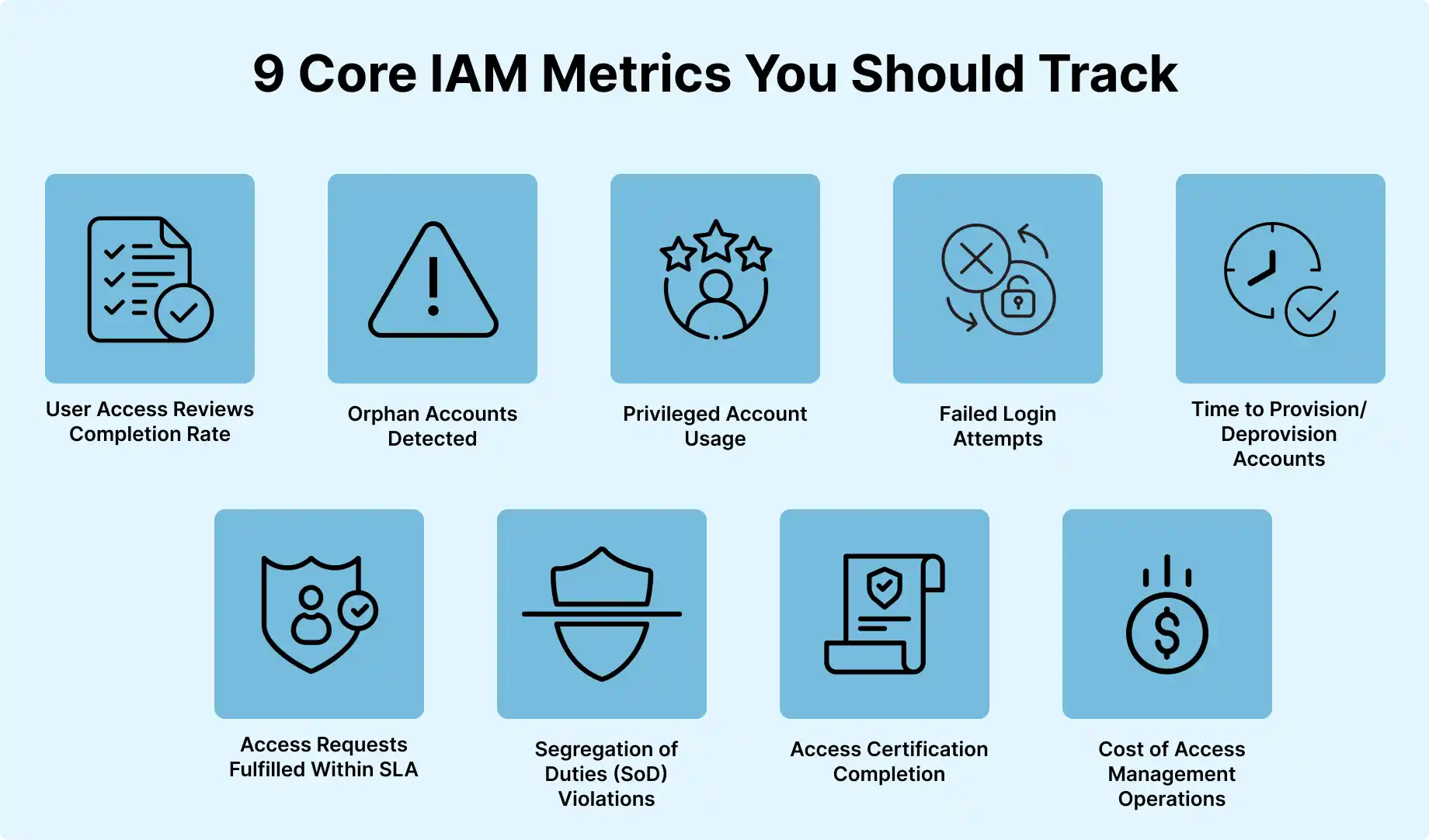
9 Core IAM Metrics for Identity Security
Tracking the right IAM metrics helps organizations strengthen security, streamline operations, and stay compliant. Here are nine core metrics every identity security program should measure:
1. User Access Reviews Completion Rate
User access reviews completion rate measures how consistently organizations verify that users still require the access they hold. It reflects whether scheduled recertifications are completed in time and ensures permissions remain aligned with current roles and responsibilities. A strong completion rate helps eliminate outdated or unnecessary access that can lead to privilege creep and compliance failures. Automating reminders, simplifying role-based reviews, and scheduling periodic checks are effective ways to maintain high completion and reduce security gaps.
2. Orphan Accounts Detected
Orphaned accounts pose a significant security risk by creating unauthorized access points to organizational resources. These accounts typically belong to employees who have left the company or contractors whose projects have ended. If not deactivated promptly, they leave the environment vulnerable to exploitation.
To address this, it is critical to ensure that accounts are properly deactivated during the offboarding process of employees and contractors. Even with automated IAM systems in place, errors, delays, or oversights can still occur.
Key metrics for identifying orphan accounts include:
- Inactive Users: Accounts not used for login within a defined period, often referred to as dormant accounts. Many organizations set the threshold at around 90 days of inactivity.
- Never-Logged-In Users: Accounts created but never actually used for login.
- Uncorrelated User Accounts (Ghost Accounts): Accounts that are not linked to any active user record.
- User Accounts with Inactive Status: Accounts marked with an inactive attribute in the IAM system, such as an employment status of "retired" or an activity status of "inactive." Reviewing these attributes helps flag potential inactivity.
3. Privileged Account Usage
Privileged accounts, such as administrator or root accounts, hold elevated permissions to critical systems and must be closely monitored. Tracking their activity helps organizations understand how often these accounts are used and by whom. Unusual usage patterns, like logins outside business hours or privilege escalations, may indicate misuse or compromise. Enforcing the principle of least privilege, enabling multifactor authentication, and logging every action are vital steps in preventing privileged account abuse.
4. Failed Login Attempts
The number of failed login attempts is a useful metric for spotting brute-force attacks, credential stuffing, or weak password practices. A sudden rise in login failures can indicate an attacker systematically guessing passwords. Establishing thresholds for failed attempts, triggering alerts, and locking accounts temporarily after repeated failures are effective defenses. Combined with MFA and rate limiting, this metric becomes a powerful early-warning indicator against external attacks.
5. Time to Provision/Deprovision Accounts
This metric tracks how long it takes to grant access to a new user or remove access when someone changes roles or leaves. Fast provisioning supports productivity, while timely deprovisioning is crucial for security. Delays in deprovisioning create windows of opportunity for unauthorized access, while provisioning delays frustrate employees and slow work. Automating lifecycle management and tying access directly to HR events improves both efficiency and compliance.
6. Access Requests Fulfilled Within SLA
Access request turnaround time shows how efficiently organizations process access approvals within defined service levels. This directly impacts user productivity and the smooth flow of business operations. Automation of low-risk requests, use of self-service portals, and clearly defined SLAs help reduce delays. Monitoring this metric helps identify bottlenecks and ensures access is delivered promptly without unnecessary administrative overhead.
7. Segregation of Duties (SoD) Violations
SoD violations occur when users are assigned conflicting roles that create opportunities for fraud or misuse, such as approving and processing the same transaction. Tracking this metric ensures that critical business processes remain free of conflicts. Auditors often flag SoD violations as high risk, making regular monitoring essential. Defining clear SoD policies, automating conflict checks, and remediating violations quickly not only reduces fraud risk but also strengthens audit readiness.
8. Access Certification Completion
Access certification measures how effectively managers or data owners review and confirm user access. Completion rates indicate whether these campaigns are being carried out as intended. High completion rates reduce the risk of unauthorized or excessive access while ensuring audit compliance. Making reviews intuitive for managers, scheduling regular certification campaigns, and escalating overdue tasks are proven ways to improve this metric.
9. Cost of Access Management Operations
This metric evaluates the expenses associated with IAM, including tool licensing, helpdesk support, manual reviews, and labor hours. It provides a clear view of how much effort and money go into managing access. Tracking these costs helps organizations identify inefficiencies and calculate the ROI of automation. By breaking down and benchmarking expenses, businesses can optimize resource allocation and demonstrate the value of IAM investments.
Benefits of Tracking IAM Metrics
Tracking Identity and Access Management (IAM) metrics goes beyond reporting numbers; it strengthens security, ensures compliance, and optimizes operational performance. By continuously monitoring these indicators, organizations gain the visibility they need to detect risks early, refine identity processes, and maximize the return on IAM investments.
1. Enhanced Security
IAM metrics give organizations real-time visibility into user activity, making it easier to spot anomalies and prevent threats before they escalate. By monitoring failed login attempts, privilege misuse, and unusual access patterns, security teams can act proactively rather than waiting for a breach. Here, the real benefit lies in being able to:
- Detect brute-force attempts, credential stuffing, or insider misuse early on
- Reduce the attack surface by eliminating orphan or unused accounts that attackers often target
- Accelerate incident response through real-time alerts tied directly to identity events
2. Regulatory Compliance
For businesses operating under SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, compliance demands ongoing proof that access policies are enforced. IAM metrics make this seamless by offering audit-ready evidence at any time, eliminating the scramble for reports during inspections. In practice, these metrics help organizations:
- Generate reliable reports that satisfy auditors quickly and accurately
- Demonstrate consistent enforcement of IAM policies across systems
- Reduce regulatory penalties while also reinforcing customer and partner trust
3. Risk Reduction
Every unchecked identity increases exposure to fraud, insider threats, or operational mistakes. IAM metrics highlight these vulnerabilities by surfacing orphan accounts, segregation of duties (SoD) violations, and unused privileges that might otherwise slip through the cracks. This means businesses can:
- Uncover and remediate orphan accounts before attackers or insiders exploit them
- Detect SoD violations that could lead to financial fraud or policy breaches
- Minimize insider threats by keeping privileged access under tighter control
- Strengthen governance and prevent gaps from surfacing during audits
4. Support Zero Trust
Zero Trust depends on continuous verification, and IAM metrics provide the insights needed to enforce it effectively. By tracking contextual access behavior, authentication trends, and privilege usage, organizations can enforce adaptive, risk-based policies. For example, metrics in a Zero Trust model enable security teams to:
- Monitor user access against device, location, and behavioral context
- Apply dynamic access decisions informed by real-time identity data
- Continuously validate privileges instead of relying on one-time approvals
5. Cost Optimization
IAM metrics aren’t just about strengthening security; they also help optimize IT spending. By surfacing inefficiencies like unused licenses, redundant entitlements, and excessive manual work, organizations can cut costs while improving efficiency. Here’s how effective monitoring creates measurable value:
- Eliminate unnecessary software licenses and duplicate access rights
- Reduce IT workload through automation and employee self-service features
- Demonstrate ROI by showing cost savings tied directly to IAM improvements
Challenges in Tracking IAM Metrics
While IAM metric offer powerful insights, organizations often struggle to measure them consistently and accurately. These challenges usually arise from structural, technical, and organizational gaps that slow down effective monitoring.
1. Data Silos
A common hurdle in IAM metric tracking comes from scattered data across multiple platforms. Identity information lives in cloud applications, on-premises systems, and HR tools, each capturing events in its own format. Because of this fragmentation, pulling everything together into a unified view becomes a major task. The lack of consolidation creates blind spots that weaken visibility and make decision-making less reliable.
2. Manual Reporting
Another issue many teams face is the reliance on outdated reporting methods. Spreadsheets and manual data pulls remain the default way of tracking IAM performance in many organizations. This approach consumes valuable time and often introduces human errors. As a result, reporting cycles drag on, accuracy suffers, and organizations find it harder to be audit-ready when regulators or stakeholders demand proof.
3. Lack of Ownership
The responsibility for IAM metrics often falls into a gray area, with different teams owning different pieces of the process. Security focuses on authentication, HR manages onboarding, and IT handles provisioning, but no one has end-to-end accountability. Without a single owner, metrics are tracked inconsistently, definitions vary across teams, and the organization never gains a complete picture of its identity security posture.
Best Practices for Improving IAM Metrics
Improving IAM metrics is not just about tracking numbers but about building a strategy that strengthens security, ensures compliance, and enhances user experience. The following best practices help transform IAM metrics into actionable levers that drive meaningful outcomes.
1. Define KPIs Aligned with Business Goals
IAM metrics are most effective when they directly support organizational objectives. Instead of focusing on vanity numbers, companies should select KPIs that improve compliance, efficiency, or user satisfaction. Clear alignment ensures that every IAM metric provides value to both IT and business stakeholders.
- Track onboarding and offboarding timelines to measure process efficiency
- Monitor authentication success rates for insights into usability and security
- Measure audit and compliance completion rates to ensure readiness
2. Automate Provisioning and Deprovisioning
Manual provisioning creates delays and security blind spots, while slow deprovisioning often leaves orphaned accounts open to exploitation. Automating the identity lifecycle minimizes risk and speeds up access for legitimate users, making IAM processes more reliable and secure.
- Reduce provisioning and deprovisioning times to improve efficiency
- Eliminate orphaned or inactive accounts through automated workflows
3. Implement MFA Everywhere
With credential-based attacks on the rise, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has become essential. Deploying MFA across all applications and systems raises the barrier for attackers while giving organizations better visibility into identity risks.
- Track MFA adoption and enforcement rates across the organization
- Monitor login success and failure trends to identify friction points
- Evaluate user experience to balance security with usability
4. Regular Access Certifications
Over time, employees accumulate excess permissions that may no longer be justified. Regular access reviews ensure adherence to the principle of least privilege while strengthening compliance posture. These certifications also help reduce risks associated with role creep and unauthorized access.
- Track completion rates of scheduled access reviews
- Monitor the percentage of permissions revoked or adjusted after reviews
5. Continuous Monitoring
IAM metrics should not be static snapshots but part of a continuous monitoring cycle. Real-time visibility into login activity, unusual access attempts, and privilege escalations enables quicker detection and response to threats.
- Measure time to detect identity-related incidents
- Track time to respond to and remediate security issues
- Monitor trends in failed or suspicious login activity
Industry Use Cases of IAM Metrics
IAM metrics are not one-size-fits-all. Each industry faces unique regulatory, operational, and security challenges that shape how these metrics are applied. By tailoring IAM measurement to specific sector needs, organizations can both enhance protection and simplify compliance.
1. Banking & Finance
In the financial sector, privileged accounts and high-value transactions are prime targets for fraudsters. Monitoring metrics such as privileged account usage and MFA adoption gives banks early warning against suspicious activity while ensuring that security remains customer-friendly. These insights also help simplify SOX and PCI DSS audits, reducing the operational strain of regulatory compliance while improving trust in digital banking systems.
2. Healthcare
Healthcare organizations must protect sensitive patient records while maintaining strict HIPAA compliance. Tracking failed logins helps detect potential credential misuse, while keeping an eye on orphan accounts ensures that only authorized staff have access to medical data. IAM metrics also support smoother access reviews, which are essential to proving compliance during audits and safeguarding patient trust in electronic health systems.
3. Retail & E-Commerce
Retailers and e-commerce companies often struggle with high employee turnover and seasonal workforce expansion. IAM metrics help measure how quickly departing employees are deprovisioned and highlight potential segregation-of-duties issues that could lead to fraud. During peak seasons, monitoring access activity becomes even more critical, as it reduces insider threats while ensuring operations run without disruption for millions of customers.
4. Technology & SaaS
Technology companies and SaaS providers must maintain customer trust while constantly adapting to evolving security standards. Metrics around risk-based authentication provide valuable insights into whether users are accessing systems from safe contexts, while automation in compliance reporting reduces audit fatigue. For organizations embracing Zero Trust, IAM metrics become the backbone of proving both security maturity and a customer-first approach.
Future of IAM Metrics: AI, Zero Trust & Real-Time Compliance
As threats evolve and digital landscapes grow more complex, the future of IAM metrics lies in real-time intelligence, behavioral insight, and rigorous trust frameworks. Metrics will move beyond simply measuring past actions to anticipating risk, enforcing Zero Trust, and ensuring continuous compliance at scale.
1. AI anomaly detection & predictive analytics to spot risks in real tim
Organizations are increasingly using machine learning and predictive models to flag unusually high-risk behavior before it leads to a breach. By analyzing historical login patterns, device usage, and access changes, AI can surface anomalies that manual reviews would miss. Over time, this enables IAM systems to shift from reactive remediation to proactive prevention, significantly shrinking the window of exposure.
2. Zero Trust trust score metrics for users, devices, and sessions
Zero Trust demands that no identity, device, or session is automatically trusted. Future IAM systems will assign trust scores based on context such as location, device posture, past behavior, and risk level. These trust scores help enforce fine-grained policies and dynamic access controls. With trust score metrics, organizations can better quantify how zero-trust their environment truly is and show progress over time.
3. Behavioral monitoring to detect insider threats and abnormal access
Metrics driven by user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) are becoming central to detecting risks originating from within. Rather than simply counting failed logins or expired credentials, future IAM metrics will chart deviation from normal behavior, such as sudden escalations of privilege, access outside typical hours, or unusual access to sensitive data. These help catch threats earlier, whether from negligent insiders or malicious actors.
4. Unified multi-cloud metrics for hybrid and SaaS environments
With many organizations running mixed environments across on-premises, multiple clouds, and SaaS, visibility becomes fragmented. IAM metrics will increasingly need to be unified by combining logs, entitlement data, device posture, and compliance state across environments. This unified view supports stronger risk assessment, simplified audit readiness, and consistent policy enforcement across all platforms.
Final Thoughts
Identity and Access Management metrics are more than just performance trackers; they’re proof of how secure, compliant, and efficient your organization truly is. In today’s identity-driven world, the right metrics turn raw data into actionable insights that help you prevent risks, simplify audits, and optimize operations.
At Tech Prescient, we help you go beyond spreadsheets and silos with real-time IAM visibility. From access reviews and deprovisioning to privileged account monitoring and Zero Trust enforcement, we ensure you measure what really matters: security, compliance, and ROI. Don’t settle for meeting audit checkboxes; use IAM metrics to strengthen your entire identity security posture.
To discover how Tech Prescient turns IAM metrics into stronger governance, resilience, and growth -
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the 4 pillars of identity and access management?
The four pillars of IAM, authentication, authorization, administration, and auditing, form the foundation of secure access. Together, they ensure the right users get the right access at the right time, while maintaining control and visibility.2. How do IAM metrics support compliance?
IAM metrics act as audit-ready proof for regulations like SOX, GDPR, and HIPAA. By tracking access reviews, SoD violations, and provisioning timelines, organizations can demonstrate compliance and avoid penalties with confidence.3. What are the 4 A’s of IAM?
The 4 A’s, authentication, authorization, administration, and audit, represent the core processes of identity governance. They help validate user identities, manage access rights, oversee identity lifecycles, and ensure accountability.4. What are the three principles of IAM?
IAM rests on three principles: verify identity, enforce least privilege, and continuously monitor. This ensures that only the right people access the right resources, with ongoing oversight to catch risks early.5. How often should IAM metrics be reviewed?
IAM metrics should be tracked continuously to spot risks in real time, but formal reviews should happen at least quarterly. This cadence supports compliance, reduces insider threats, and keeps your IAM program audit-ready.