IAM Implementation Plan: Steps & Best Practices

An identity and access management implementation plan isn’t just another IT task, but a key part of keeping your organization secure. A proper IAM implementation ensures that the appropriate people are granted the relevant rights. IAM systems safeguard sensitive information and uphold trust in digital transactions. By ensuring that only authorized users have access, IAM strengthens security and protects valuable data. It streamlines user account management, simplifies permission assignments, and minimizes vulnerabilities effectively.
A well-structured identity and access management (IAM) strategy enables organizations to manage users efficiently, enforce security policies, and deliver a seamless user experience. This has become even more critical in today’s environment, where remote work and cloud adoption are the norm. Establishing strong controls over access while maintaining user flexibility is essential for balancing security and productivity.
In this blog, we’ll explore IAM tools and services that help optimize identity processes. We’ll cover key steps, requirements, common challenges, and practical recommendations to strengthen your IAM framework.
According to a 2025 IAM report by Tenfold Security, 80% of cyberattacks use identity-based methods, and 80% of organizations believe better identity and access management could have prevented some or all of these attacks. That’s a strong reminder of how important IAM is for protecting your organization from modern threats.
Key Takeaways:
- Learn what IAM implementation really is and why it’s important for your organization
- Discover a clear, step-by-step process for deploying IAM successfully
- See how best practices like Zero Trust, least privilege, and automation make IAM more effective
- Find practical ways to handle common IAM challenges
- Explore what’s next for IAM, including AI, continuous authentication, and cloud-native adoption
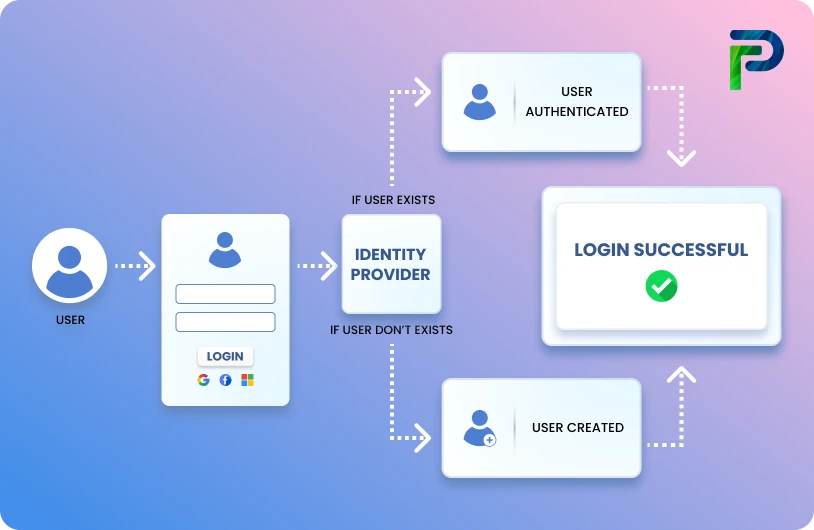
What Is IAM Implementation?
IAM implementation refers to the process of establishing and integrating policies, procedures, and technologies that ensure only authorized individuals can access specific systems and resources. It combines identity management, access management, and governance practices to create a secure and compliant environment.
To achieve this, organizations rely on several key components that work together as part of a structured IAM framework.
-
Identity Management ensures that every user, system, or service has a unique digital identity associated with defined attributes, roles, and permissions, which collectively determine access rights.
-
Authentication verifies the legitimacy of users or entities attempting to access resources through methods such as passwords, biometrics, security tokens, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
-
Authorization defines what actions or resources an authenticated user is permitted to access, typically enforced through role-based access control (RBAC) or access control lists (ACLs).
-
Account Lifecycle Management governs the entire user lifecycle journey, covering creation, modification, and deactivation to ensure access is provisioned correctly and revoked when no longer needed.
-
Privileged Access Management (PAM) provides additional layers of security for accounts with elevated privileges, such as administrators or super-users. By controlling, monitoring, and auditing privileged sessions, PAM helps prevent insider threats, privilege misuse, and unauthorized access to critical systems.
-
Asset Management ensures that all devices, applications, and digital resources within the IT environment are properly inventoried and linked to the right user identities. This helps organizations gain better visibility into who is accessing which assets, enforce policies consistently, and reduce shadow IT risks.
-
Identity governance focuses on monitoring user activities, identifying unauthorized access attempts, and maintaining compliance with data security regulations. It enables organizations to enforce and manage access policies efficiently, reduce risks linked to privilege misuse, and ensure adherence to regulatory standards like GDPR and PCI-DSS.
-
Audit and Compliance delivers detailed visibility into user activity by tracking and reporting who accessed what, when, and how, thereby enabling organizations to meet both internal security requirements and external regulatory mandates.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO) simplifies access by allowing users to authenticate once and securely use multiple applications and systems, improving user experience while reducing password-related risks.
Together, these components establish a resilient IAM system that protects sensitive data, mitigates risks, ensures regulatory compliance, and delivers a seamless user experience.
Phases of IAM Implementation
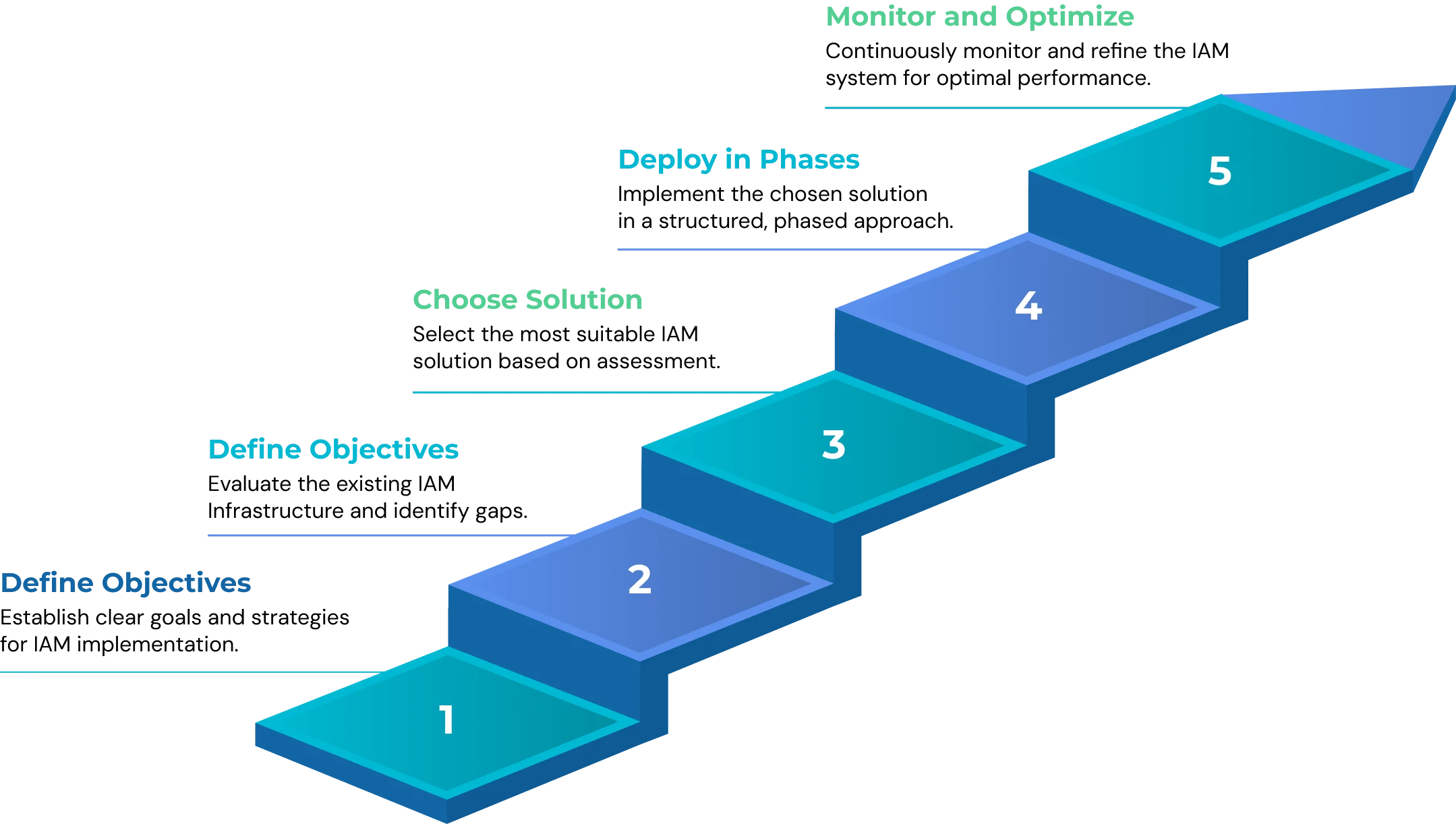
IAM implementation progresses through well-defined phases, each focusing on strategy, technology, and continuous improvement. This structured approach helps organizations strengthen access control, improve compliance, and minimize risks. The process usually includes stages like:
Step 1. Assess Current Technology Landscape
A strong IAM implementation starts with a clear understanding of your existing technology environment. This initial assessment is essential for uncovering integration challenges and identifying opportunities for improvement.
Begin by mapping your entire application ecosystem, including cloud-based SaaS platforms, on-premise legacy systems, and custom-built applications. Capture all user access points, whether through VPN connections or public-facing apps. Special focus should be given to authentication mechanisms and user directories, since these components will require careful integration or migration into the new IAM framework.
Equally critical is evaluating your current security posture. Review existing access controls, security policies, and compliance practices to highlight gaps that must be addressed. Documenting past security incidents or access-related issues can also provide valuable insight into areas needing priority attention during the IAM rollout.
Step 2. Define Objectives & Strategy
A strong IAM program begins with developing a comprehensive strategy that aligns with your business objectives. The foundation of this strategy lies in setting clear objectives and success metrics. These could include reducing security incidents, improving user satisfaction, and decreasing help desk tickets related to access issues. Compliance requirements such as GDPR and PCI-DSS should also be factored in, but positioned after core objectives are established.
Achieving these goals requires engaging stakeholders early and developing a roadmap that addresses the entire user lifecycle. Policies should cover key aspects like multi-factor authentication, password requirements, session management, and emergency access, striking the right balance between strong security and smooth usability.
Step 3. Choose the Right IAM Solution
Selecting the right IAM platform is a critical decision that goes beyond technical specifications. When evaluating solutions, organizations should consider not only scalability, compliance, and integration needs but also the vendor’s track record, quality of support, comprehensiveness of documentation, and level of community engagement. The solution should support essential capabilities such as Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and privileged access management (PAM), while also being flexible enough to scale with your organization’s future growth.
Ensure seamless integration with HR systems and align the solution with Zero Trust principles, so access decisions are dynamic and context-aware. Beyond technical specifications, evaluate vendor support, documentation quality, and scalability for long-term fit.
Step 4. Deploy in Phases
Deployment should be done step by step to avoid disruption and ensure smooth adoption. Start with a proof of concept to test authentication, directory synchronization, and provisioning workflows. Next, run a pilot with a small group of users, collect feedback, and fine-tune the setup. Finally, roll it out across the enterprise. This way, integration issues are caught early and users get time to adjust.
Step 5. Integrate with Existing Systems
After phased deployment, the next step is to integrate IAM with existing enterprise systems and applications. This makes sure access policies are applied consistently across the technology stack, avoiding gaps and overlaps. Key integrations include HR platforms for automated provisioning and CRM/ERP systems for role-based access. Seamless integration strengthens identity governance, simplifies user lifecycle management, and ensures IAM works as a central hub instead of a standalone tool.
Step 5. Continuous Monitoring & Optimization
Implementation does not end at deployment. Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential for long-term effectiveness. Deploy monitoring tools to track user access patterns, detect anomalies, and generate compliance reports. Automate key processes such as onboarding, offboarding, and periodic access reviews. For example, automating employee onboarding ensures new hires immediately receive the right level of access, while automated offboarding revokes credentials instantly when employees leave, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Regular audits and policy reviews help keep the IAM system aligned with evolving security threats and regulatory requirements. Over time, continuous improvement ensures IAM remains a business enabler, not just a security control.
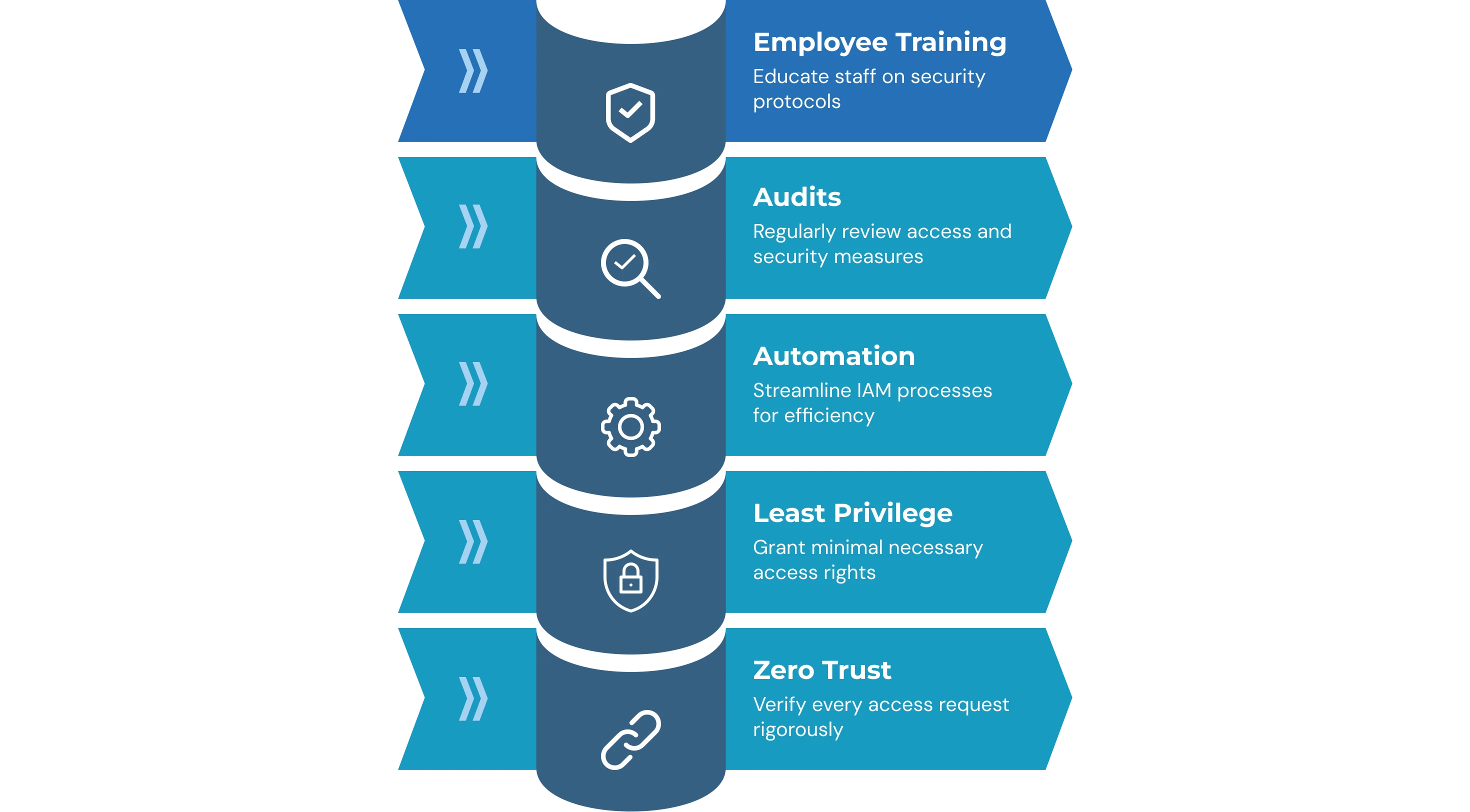
Best Practices for IAM Implementation
Successfully implementing an IAM solution requires more than following the implementation steps. Organizations must adopt best practices to ensure comprehensive security, reduce risks, and maximize efficiency. Key practices include:
1. Adopt Zero Trust Principles
Implement IAM within a Zero Trust framework, where no user or system is inherently trusted. Every access request should be continuously verified based on identity, context, and device. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and ensures that security policies adapt dynamically to evolving threats.
2. Enforce Least Privilege Access (POLP)
Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) by ensuring users have only the minimum access rights required to perform their roles. Continuously review and adjust permissions to avoid privilege creep, where unnecessary rights accumulate over time. By enforcing POLP, organizations not only shrink the attack surface but also limit the damage potential of compromised accounts, strengthening overall security posture.
3. Automate Provisioning and Deprovisioning
Leverage automation to streamline user onboarding and offboarding. Automated provisioning ensures new employees receive appropriate access immediately, while deprovisioning revokes permissions promptly when roles change or employees leave. Using workflows integrated with your identity provider simplifies management and enhances security.
4. Conduct Regular Audits and Certifications
Establish regular reviews of access rights, security policies, and compliance requirements. Conduct audits to verify that users’ permissions align with their roles and that the system adheres to internal and external regulations. Periodic certifications help maintain accountability and ensure continuous alignment with organizational security objectives.
5. Train Employees on IAM Usage
Provide comprehensive training to IT personnel, department heads, and end users on the IAM system and related processes. Educated users are better equipped to follow policies, leverage automation, and avoid common security pitfalls, ensuring that IAM delivers both operational efficiency and protection.
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Implementing IAM offers significant benefits, but organizations often face challenges that must be addressed for a successful deployment.
1. Resistance to Adoption
Employees may resist adopting a new IAM system due to unfamiliarity or perceived inconvenience. This challenge can be overcome through comprehensive training programs for IT teams and end users. By demonstrating the benefits of IAM, explaining security implications, and guiding users through new workflows, organizations can encourage adoption and ensure consistent policy adherence.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
Integrating IAM solutions with existing technology stacks can be complex and time-consuming. A phased migration approach helps organizations gradually incorporate legacy applications, directories, and authentication mechanisms into the new system. This strategy allows testing and refinement at each step while minimizing operational disruptions.
3. Over-Permissioning
Providing users with more access than necessary increases security risks and complicates compliance. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that users receive only the permissions required for their roles. Coupled with regular access reviews and automated provisioning, this approach enforces least privilege principles and reduces the likelihood of privilege creep.
Benefits of IAM Implementation
Adopting an IAM solution delivers both security and operational efficiency. Below are the core advantages organizations gain:
1. Stronger Security and Streamlined Operations
With IAM, access management is centralized across the enterprise. Rather than configuring access rights separately for each system or application, administrators can use a single platform to define, enforce, and monitor policies consistently. This unified approach reduces administrative overhead for onboarding, offboarding, and access adjustments while ensuring uniform enforcement of controls, minimizing gaps or errors that could expose security vulnerabilities.
2. Compliance Made Easier
IAM platforms play a critical role in meeting industry regulations by maintaining detailed audit trails and enforcing strict access controls. This capability is vital for sectors bound by standards such as HIPAA in healthcare or SOX in finance. By generating comprehensive access logs, IAM enables organizations to demonstrate compliance, avoid legal complications, and reduce the risk of costly penalties.
3. Lower IT Support Burden
Automating provisioning and deprovisioning significantly cuts down routine IT workloads. Self-service features like password resets and access requests allow users to resolve common issues on their own. This independence reduces dependency on IT support teams, lowering support costs and freeing up technical staff to focus on higher-value tasks.
4. Proactive Risk Reduction and Future-Readiness
IAM enforces the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP), ensuring users hold only the exact access rights required for their responsibilities. This minimizes exposure to both insider and external threats. In addition, IAM solutions scale seamlessly as organizations expand, supporting new users, devices, and applications while maintaining consistent security standards across the environment.
IAM Implementation Example
A mid-sized organization faced challenges with manual identity and access management. Onboarding new employees required IT to create accounts across multiple systems, assign permissions manually, and track access requests using spreadsheets. This process was slow, prone to errors, and often resulted in inconsistent access, making compliance and security harder to maintain.
To address these issues, the organization integrated its HR system with IAM and automated the workflows. New hires received immediate access to all required resources, while role changes and offboarding triggered automatic updates to permissions. This automation reduced errors, ensured consistent access control, improved security, and freed IT teams to focus on strategic tasks. The result was faster onboarding, stronger compliance, and a streamlined, secure IAM process.
Final Thoughts
IAM implementation is no longer just an IT initiative; it is a strategic enabler of security, compliance, and operational efficiency. As organizations face rising cyber threats and complex access environments, adopting a structured IAM plan ensures that only the right users have the right access at the right time, keeping your business secure, agile, and compliant.
At Tech Prescient, we simplify IAM with expert guidance, proven frameworks, and automation-first solutions. We help close security gaps, streamline access, and build a future-ready identity foundation.
Don’t let identity risks or complexity slow your business. Start your journey toward secure, seamless IAM with Tech Prescient today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an IAM implementation plan?
An IAM implementation plan is essentially a structured roadmap for deploying Identity and Access Management solutions across your organization. It helps ensure that user access is properly secured, managed, and aligned with your business and security goals. By following a plan, you can avoid gaps, reduce risks, and make the rollout much smoother.2. What are the steps of IAM implementation?
Implementing IAM usually follows a few clear steps: start with strategy and goal setting, assess your current systems and access policies, select the right IAM solution, deploy it in phases, and finally, set up continuous monitoring. This step-by-step approach makes adoption easier and more effective.3. What are the 4 pillars of IAM?
The four pillars of IAM are Authentication, Authorization, Administration, and Audit. Authentication ensures users are who they claim to be, Authorization controls what they can access, Administration handles user and policy management, and Audit tracks all actions for compliance and security visibility. Together, they form the backbone of a strong IAM system.4. How to implement IAM effectively?
To implement IAM effectively, start small with key systems, automate repetitive processes like provisioning and deprovisioning, enforce least privilege access for users, and continuously monitor activities and policies. This approach helps you secure your environment without overwhelming your IT team.5. What tools are commonly used for IAM implementation?
Common IAM tools include solutions like Okta, Microsoft Azure AD, SailPoint, and ForgeRock. These tools help with identity lifecycle management, single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and compliance tracking, making it easier to manage users and secure access across your organization.