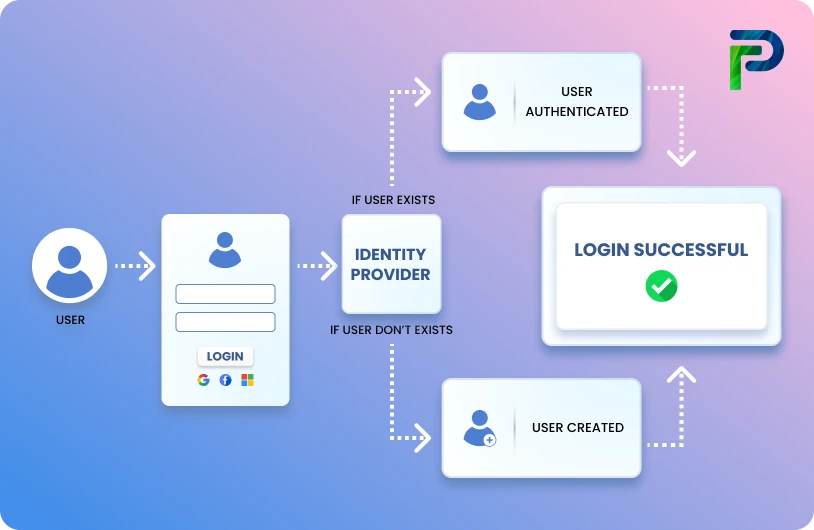
Workforce Identity and Access Management (IAM) Explained

Workforce Identity and Access Management is a security framework that governs how employees, contractors, and business partners access organizational systems and data throughout their employment lifecycle. It automates identity provisioning, enforces access policies, and maintains audit trails to ensure the right people have appropriate access to the right resources at the right time.
The need for robust workforce IAM has become critical, as 78% of companies experienced identity-related data breaches, according to Veritis' IAM Trends Report 2025, that negatively impacted their operations. Additionally, with 32.6 million Americans who work remotely, according to Neat's State of Remote Work 2025 report, representing 22% of the U.S. workforce, organizations need identity-centric security that adapts to distributed work environments while maintaining governance standards.
Workforce Identity and Access Management transforms security from a barrier into an enabler, allowing organizations to scale securely while reducing operational overhead and compliance risks through automated, policy-driven access controls.
Key takeaways:
- WIAM secures employee access through policy-driven controls that automatically adjust based on user roles, risk levels, and contextual factors
- Enhances productivity with SSO & lifecycle automation, eliminating password friction and manual provisioning delays
- Supports compliance (HIPAA, GDPR, SOX) through automated audit trails and continuous policy enforcement
- Enables Zero Trust strategies by implementing identity-centric security that verifies every access request
What is Workforce Identity and Access Management?
Workforce Identity and Access Management is a security discipline that encompasses the policies, processes, and technologies used to manage digital identities and control access to organizational resources for employees, contractors, and business partners.
Its primary purpose is to regulate how workforce members and business partners securely access and utilize organizational or business resources and how their identity and account data are stored. By implementing workforce IAM, businesses can safeguard their sensitive data from breaches and cyber-attacks. This comprehensive system empowers IT administrators to oversee workforce identities effectively, ensuring secure access to applications and various other resources for employees and partners.
The core distinction lies in how workforce IAM treats identity as a dynamic, contextual attribute rather than a static credential. Traditional access control systems grant permissions based on initial authentication, while workforce identity management continuously evaluates access decisions based on changing risk factors and business context.
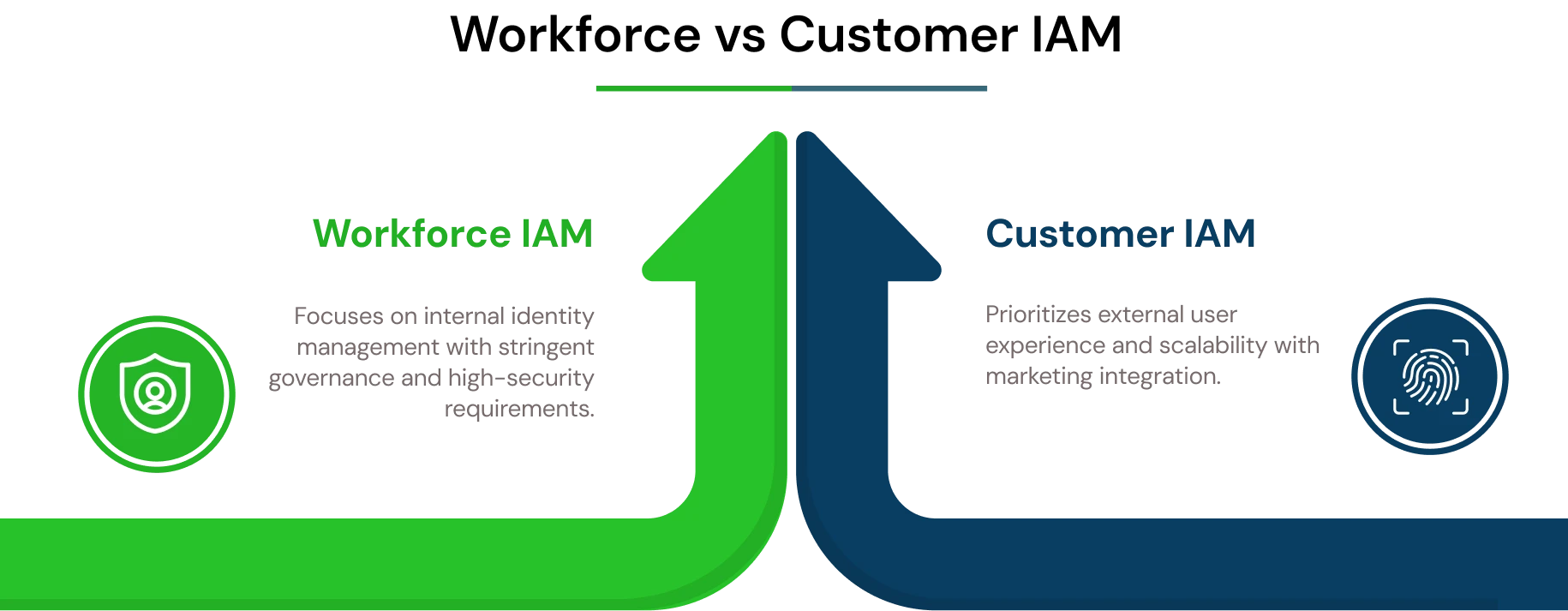
Unlike Customer IAM (CIAM), workforce IAM emphasizes governance, compliance, and risk management for internal users who require deep access to organizational systems. This focus addresses the reality that one in two data breaches emanate from bad identity and access management capabilities according to Thales' IAM Predictions 2025 report.
The modern workforce access management approach recognizes that 49% of organizations expect the number of identities they manage to increase by three times or more, according to Expert Insights' 2025 Identity Security Stats, primarily driven by non-human machine identities.
Core Components of Workforce IAM
Workforce IAM platforms integrate six foundational components that collectively create comprehensive identity governance across enterprise environments.
1. Identity Lifecycle Management
Account Provisioning & Deprovisioning - The lifecycle begins before an employee's first day through HR system integration that pre-provisions accounts and access based on role assignments. When Sarah joins as a Marketing Manager, the system automatically creates accounts in Active Directory, Office 365, Salesforce, and marketing-specific tools with appropriate role-based access control permissions.
Account Data Management and Storage - Encrypt stored identity data, follow industry standards, and keep storage methods updated. This prevents unauthorized access and protects sensitive user information throughout the employment lifecycle, ensuring identity data remains secure from creation to deletion.
Data Accuracy and Consistency - Use audits, validation checks, and synchronization to keep identity data correct and consistent across all systems. This avoids errors that could create security gaps and ensures a strong IAM system by maintaining reliable identity information as roles and access requirements change.
Organizations implementing comprehensive identity lifecycle management report 40% reduction in help desk tickets according to Forrester's Total Economic Impact study related to access provisioning, while significantly improving secure employee access through consistent, immediate updates and reliable identity data management.
2. Authentication & Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On is an authentication method that allows users to access multiple applications using a single set of credentials, eliminating password management complexity. Modern SSO implementations provide centralized security controls and comprehensive audit capabilities.
The technical foundation relies on security protocols like SAML 2.0, OAuth 2.0, and OpenID Connect to establish trust relationships between identity providers and applications. These protocols are the backbone of modern authentication systems, offering businesses a way to simplify the user experience while maintaining robust security through identity management. SSO provides centralized policy enforcement, allowing consistent authentication requirements and access controls across all connected applications.
Comprehensive SSO implementations covering primary business applications save employees substantial time daily while reducing password-related help desk tickets significantly, improving overall workforce access efficiency.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication is a security method requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access, significantly reducing unauthorized access risk even when primary credentials are compromised.
Security research demonstrates that MFA blocks 99.9% of automated attacks according to Microsoft Security Blog that rely on stolen or weak passwords. This effectiveness stems from the practical difficulty of simultaneously compromising multiple authentication factors.
Risk-based or adaptive MFA represents evolution beyond static authentication requirements, analyzing contextual factors like device trust levels, geographic location, and application sensitivity to determine appropriate authentication strength for secure employee access.
4. Role-Based & Attribute-Based Access Control (RBAC/ABAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) assigns permissions to users based on organizational roles, while Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) incorporates additional attributes like time, location, and resource characteristics for access decisions.
RBAC creates access permissions based on job functions rather than individual users. A "Financial Analyst" role includes access to accounting systems and financial reporting tools, but excludes HR systems or engineering environments. This approach simplifies access management by grouping permissions logically.
ABAC adds contextual intelligence through attributes beyond role assignments, including time restrictions, location controls, device trust levels, or data classification requirements, creating dynamic access control policies.
5. Directory Sync & Integrations
Directory synchronization refers to automated processes maintaining consistent identity information across multiple systems and directories, ensuring user data and access permissions remain accurate across the technology ecosystem.
Organizations typically maintain user information in HR systems like Workday, directory services like Active Directory, cloud applications with separate user databases, and legacy systems. Without synchronization, these systems develop conflicting information creating security gaps.
Modern directory sync platforms support complex mapping and transformation rules accommodating differences in data formats and organizational structures, enabling unified identity management necessary for comprehensive security governance.
6. Audit, Reporting & Compliance
Audit and reporting capabilities encompass systems and processes that track, analyze, and document all identity-related activities to support security monitoring, compliance IAM requirements, and governance oversight.
Comprehensive audit trails capture every identity event including authentication attempts, access grants, and administrative actions. This granular logging provides forensic capabilities necessary for security investigations and regulatory compliance demonstration.
SOX compliance alone requires organizations to spend over $1 million annually according to IBM's SOX Compliance guide, with many spending $1-2 million annually according to Zluri's SOX Compliance Cost report on directly identifiable compliance costs. Automated systems generate reports continuously, reducing manual effort while improving accuracy.
Benefits of Workforce IAM for Enterprises
Workforce IAM delivers measurable value across security, operational efficiency, cost reduction, and compliance management.
- Enhanced Security - Modern workforce identity management platforms reduce identity-related security incidents through automated access controls and continuous monitoring. IAM solutions administer user permissions, guaranteeing the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. Through stringent access controls, these systems ensure that data remains confidential, unmodified, and readily accessible only to authorized personnel. By implementing these robust security measures, IAM solutions safeguard data integrity and prevent unauthorized access, providing comprehensive protection against data breaches and cyber threats. Identity governance addresses human factors contributing to successful cyber attacks through automated provisioning, principle of least privilege enforcement, and continuous behavioral monitoring that detects unusual access patterns before they escalate into security incidents.
- Improved Productivity - SSO implementations reduce help desk tickets significantly while eliminating productivity drains from password management. Identity lifecycle management eliminates delays preventing new hires from accessing required resources, with comprehensive automation enabling faster employee productivity through pre-configured role-based access control.
- Lower Costs - Automation reduces IT operational overhead significantly with organizations typically seeing ROI within 12 months according to Forrester's Total Economic Impact study. SSO implementations reduce password reset requests substantially while improving security through centralized credential management.
- Compliance Ready - Automated audit trails and policy enforcement ensure continuous compliance with HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR. Organizations avoid substantial compliance violation costs through proactive governance & compliance capabilities preventing violations rather than detecting them after occurrence.
- Support for Remote Workforce - Zero Trust architectures enabled by workforce IAM allow secure access from any location without VPN dependencies. This flexibility supports hybrid work models that 83% of employees prefer globally, according to Neat's State of Remote Work report while maintaining enterprise security standards.

Workforce IAM vs. Traditional IAM
The distinction between workforce-focused IAM and traditional IAM approaches reflects fundamental differences in scope, governance requirements, and risk management strategies.
Workforce IAM = focused on employees/contractors requiring deep system access with high compliance and audit requirements. IAM = broader scope (customers, partners, external) with moderate governance and mixed risk levels.
| Aspect | Workforce IAM | Traditional IAM | CIAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Users | Employees, contractors, internal staff | Mixed internal/external | External users, customers, partners, end-users |
| Access Depth | Deep system access, Admin privileges, Enterprise apps (ERP, HR) | Varies by use case | Limited profile access, Transactional data only |
| Governance Focus | Role design, Segregation of duties, Privileged access reviews | Moderate governance | Consent management, Privacy compliance, GDPR/CCPA focus |
| Risk Profile | Insider threats, Regulatory violations, Financial fraud potential | Mixed risk levels | Account takeover, Credential stuffing, Customer trust risk |
| Lifecycle Complexity | Complex onboarding/offboarding, Role changes & transfers, Entitlement creep management | Varies | Simple registration, Profile updates, Basic deletion |
| Audit Requirements | SOX, HIPAA, PCI audits, Detailed access logs, Periodic recertifications | Moderate auditing | Privacy audits, Consent tracking, PII management |
Common Challenges in Workforce IAM
Organizations implementing workforce IAM encounter predictable challenges requiring strategic planning and architectural considerations.
- Managing hybrid IT environments - 89% of organizations operate multi-cloud environments according to Flexera's 2024 State of Cloud report with both legacy on-premises systems and modern SaaS applications. Each platform uses different authentication protocols requiring sophisticated middleware for unified identity management.
- Balancing security with UX - 67% of employees report security measures negatively impact work efficiency according to Expert Insights' Identity Security Stats, leading to shadow IT adoption circumventing security policies.
- Onboarding contractors/freelancers securely - These users need temporary access with clear expiration dates, limited privileges, and simplified onboarding processes without compromising secure employee access standards.
- Avoiding over-permissioning - Access creep occurs when users accumulate permissions over time without corresponding removals as roles evolve, creating unnecessary security exposure and compliance IAM risks.
Leading Workforce IAM Solutions in 2025
Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence represents next-generation identity governance built specifically for digital-first enterprises requiring comprehensive workforce identity management without traditional implementation complexity. The platform combines intelligent automation, real-time policy enforcement, and audit-ready compliance in a cloud-native architecture.
Key Capabilities:
- AI-Powered Access Decisions - Analyzes user behavior patterns and risk indicators to automatically adjust access permissions in real-time, eliminating manual access reviews while improving security through continuous monitoring
- Extensive Integration Support - Pre-built connectors support over 50 enterprise applications, including Salesforce, Azure AD, Google Workspace, and SAP, enabling comprehensive workforce access management without custom development
- Visual Policy Builder - Allows business users to define complex RBAC/ABAC rules without technical expertise, translating business requirements directly into enforceable security policies
- Automated Lifecycle Management - Handles complex joiner-mover-leaver processes while maintaining granular access controls and comprehensive audit trails
- Proactive Risk Management - Machine learning capabilities identify unused entitlements, access anomalies, and potential security risks before they become incidents
For organizations evaluating workforce IAM solutions, consider reading our comprehensive comparison of IGA vs IAM approaches to understand which architectural model best fits your requirements.
Best Practices for Implementing Workforce IAM
Enforce least privilege - Grant users only minimum permissions required for current role responsibilities. Regular access reviews every 90 days ensure permissions remain appropriate as roles evolve and organizational structures change.
Automate lifecycle management - Deep integration with HR systems enables automatic provisioning, role changes, and deprovisioning based on employment status changes. This automation eliminates security gaps and improves secure employee access through immediate updates.
Regular access reviews - Quarterly reviews for standard users and monthly reviews for privileged accounts ensure access remains aligned with business requirements and compliance IAM policies using automated workflows requiring explicit approval decisions.
Integrate HR systems with IAM - Comprehensive integration creates single source of truth for employee data, role assignments, and organizational structure enabling dynamic access control policies automatically adjusting as employees change departments or responsibilities.
Adopt Zero Trust principles - Implement identity-centric security treating every access request as potentially compromised, requiring continuous verification and contextual access decisions regardless of user location or device trust.
Ready to get started?
See how our AI-powered platform, Identity Confluence, can automate your identity governance by implementing these components with visual policy builders and automated workflows
The Future of Workforce IAM (2025 & Beyond)
Access decisions relying on AI-driven insights - A Scoop Market February 2021 report forecasts that by 2025, at least 50% of IAM platforms are going to leverage AI-driven analytics to detect anomalies, automate identity access provisioning, and provide insight into potential exposures or breaches.
Passwordless authentication adoption - 30% of consumers have already implemented passkey authentication methods according to Thales' IAM Predictions 2025, with banking and financial services leading adoption due to regulatory compliance and security benefits.
Deeper integration with Zero Trust - By 2026, over 60% of enterprises are projected to adopt Zero Trust frameworks according to Scoop Market's research within their workforce IAM systems, focusing on securing access regardless of user location or device.
Cloud-native IAM solutions - Cloud-native platforms dominate new implementations prioritizing scalability, rapid deployment, and integration capabilities. These platforms leverage cloud infrastructure for global availability and simplified management compared to traditional systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the 5 key components of IAM?
The four pillars are:- Authentication - verifying user identities
- Authorization & Access Control - granting appropriate permissions
- Identity Lifecycle Management - onboarding, role changes, and offboarding
- Governance & Compliance - monitoring access for security and regulations
2. How does workforce IAM differ from customer IAM?
Workforce IAM manages access for internal users like employees and contractors, while Customer IAM (CIAM) manages external users such as customers or partners. Workforce identity management focuses on productivity, compliance, and security for staff, whereas CIAM focuses on user experience and customer engagement.3. Which certifications are best for identity and access management?
Top IAM certifications include:- Certified Identity and Access Manager (CIAM)
- Identity Management Institute (IMI) Certifications
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) with IAM focus
- Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator Associate
4. What are examples of workforce IAM tools?
Popular workforce IAM tools include Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence for comprehensive identity governance, Microsoft Entra ID for Microsoft ecosystems, Okta Workforce Identity for extensive integrations, and SailPoint IdentityNow for advanced governance capabilities.