What Is Automated Lifecycle Management?

Introduction
In today’s ever versatile digital ecosystem, automated lifecycle management (ALM) has become more than just a technical convenience; it can be considered a cornerstone of strong identity governance framework. From the moment a user joins an organization to the day their access is revoked, every stage in their identity lifecycle must be managed with utmost precision.
The challenge? Manual processes simply can’t keep up. They’re slow, error-prone, and leave major gaps that can compromise security and compliance. This is where identity automation steps in, transforming a traditionally tedious process into a one that’s streamlined, consistent, and secure.
At Tech Prescient, we see ALM as a natural extension of Identity Governance and Administration (IGA). By automating the provisioning, updating, and deprovisioning of user access, organizations not only save time and reduce human error but also enforce compliance policies effortlessly across applications, data, and systems. In a world where the security perimeter is defined by identities, automation isn’t just an upgrade, to have, it’s a necessity.
Keytakaways
You’ll learn how automated lifecycle management:
- Automates user, app, and data lifecycles — covering everything from onboarding and provisioning to updates, deprovisioning, and data retention.
- Improves compliance and auditability — with consistent policy enforcement, detailed logs, and audit-ready reporting.
- Reduces manual errors and IT workload — by replacing repetitive, error-prone tasks with streamlined, automated workflows.
- Supports Zero Trust and identity governance — ensuring least-privilege access, role-based controls, and continuous verification across your IT ecosystem.
What Is Automated Lifecycle Management?
Automated Lifecycle Management (ALM) is the practice of using technology to handle repetitive, rule-based events in a user, application, or data lifecycle without manual intervention. Think of it as a behind-the-scenes engine that ensures the right actions happen at the right time, always.
In the context of identity governance, ALM covers everything from provisioning a new employee’s access on day one to automatically updating permissions when their role changes to securely revoking access the moment they leave the organization. But it doesn’t stop at identities, ALM also manages software updates, license renewals, and data retention policies across the entire IT ecosystem.
The goal is simple: improve efficiency, strengthen security, and maintain compliance without adding to your IT team’s workload. By automating these lifecycle events, organizations can:
- Eliminate human error in high-volume processes
- Reduce operational costs
- Ensure consistent policy enforcement across users, applications, and data
- Free up teams to focus on strategic priorities instead of repetitive tasks
Whether it’s ensuring identity automation in your IGA framework, managing application lifecycles, or enforcing data governance rules, ALM turns what was once a manual, error-prone process into a streamlined, policy-driven workflow that works 24/7.
Why Lifecycle Automation Matters in Modern Enterprises
Today’s enterprises juggle a growing mix of on-premises systems, cloud applications, and remote users. With hybrid workforces becoming the norm and compliance demands evolving at record speed, manual lifecycle management simply can’t keep up.
Automation changes the game by making governance scalable and sustainable. It ensures that every identity, application, and dataset is managed consistently, whether you’re onboarding a new hire, rolling out software updates, or enforcing data retention rules.
The impact is immediate:
- Fewer Errors: Automated processes remove the risk of missed steps or incorrect permissions.
- Consistent Policy Enforcement: Role-based access controls (RBAC), least privilege, and zero-trust policies are applied the same way every time.
- Less IT Friction: No more bottlenecks for access requests or deprovisioning; IT teams can focus on strategy instead of repetitive admin work.
With automated lifecycle management, security risks like lingering access for former employees are eliminated, onboarding becomes seamless, and audit outcomes improve thanks to stronger IT general and application controls. For modern enterprises, automation isn’t just a convenience; it’s a foundation for secure, compliant, and efficient operations.
“The true value of automated lifecycle management isn’t just in speeding up processes, it’s in making every identity decision intelligent and auditable. When ALM is embedded into your IGA strategy, access rights are granted, modified, and revoked with the same precision every single time, regardless of scale. That’s how organizations move from reactive compliance to proactive governance and from security gaps to zero blind spots.”
— Tech Prescient Expert Team
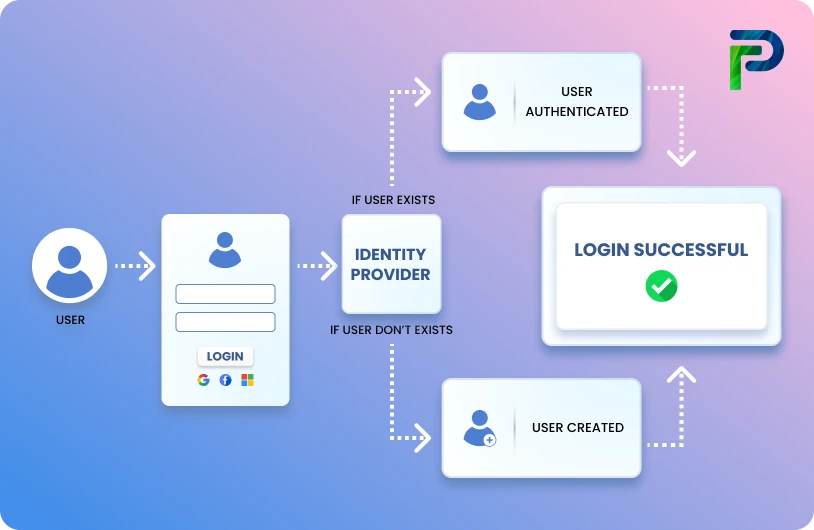
How Does Identity Lifecycle Management Work?
Identity lifecycle automation orchestrates every stage of a user’s journey within an organization from the moment they join, to the day they leave ensuring that access is provisioned, modified, reviewed, and revoked with speed and accuracy.
At its core, it integrates HR systems (where employee records originate) with IT systems (where access is granted) so that identity changes are triggered automatically based on role, department, or employment status. Here’s how it works across the key stages:
- Onboarding
When HR adds a new hire to the system, the automation engine provisions accounts, assigns role-based permissions, and delivers access to all necessary applications, databases, and tools often before the employee’s first day. - Role Changes & Transfers
If an employee is promoted, moved to a new team, or changes responsibilities, their access is automatically updated to match their new role, while removing permissions no longer needed. This prevents role creep and enforces least privilege policies. - Access Reviews
Regular, automated access reviews ensure that each user’s permissions remain aligned with compliance standards like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOX, and GDPR. This step reduces audit loop holes and strengthens governance controls. - Offboarding
Once HR processes a termination or contract end, the automation instantly revokes all system and data access, closes accounts, and archives records according to data retention policies. This mitigates the security risks posed by lingering credentials.
By connecting people processes in HR with technology governance in IT, identity lifecycle automation eliminates manual handoffs, reduces security gaps, and ensures that policy enforcement happens the same way — every single time.
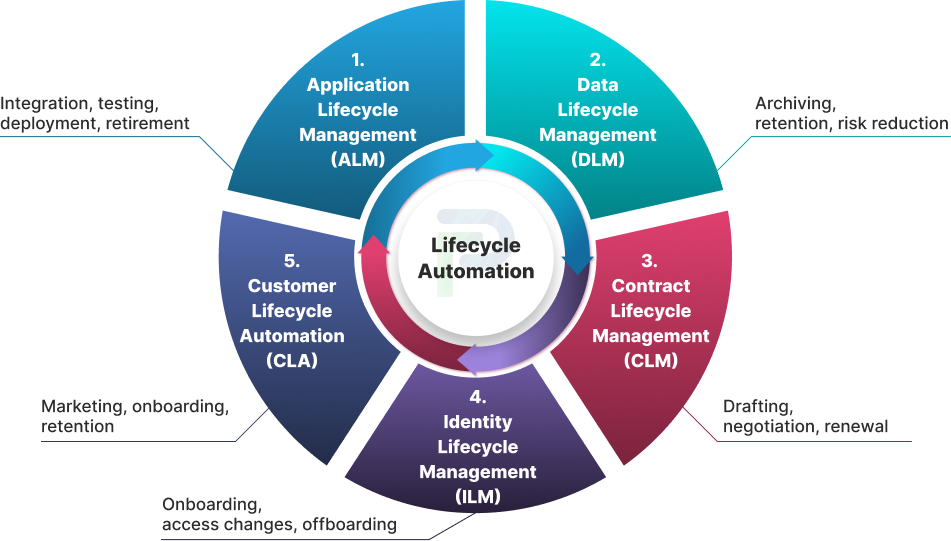
Other Lifecycle Automation Use Cases
Lifecycle automation isn’t limited to managing user identities. The same principles consistency, efficiency, and policy-driven workflows, can transform other critical business functions. From software delivery to contract management, automation ensures speed, accuracy, and compliance across the board.
1. Application Lifecycle Management (ALM)
Application Lifecycle Management covers the entire journey of an application from its initial development to eventual retirement. Automation streamlines repetitive yet essential steps, such as:
- Integration & Testing: Automatically integrate new code, run test cases, and validate quality before deployment.
- Deployment: Push updates or new applications to production environments with minimal downtime.
- Retirement: Remove obsolete applications securely while preserving necessary records.
For DevOps teams, ALM automation is the backbone of high-velocity CI/CD pipelines, ensuring faster releases, fewer errors, and better alignment between development and operations.
2. Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)
Data is both an asset and a liability if not managed properly. Data Lifecycle Management automation handles information from creation to secure disposal:
- Archiving: Move inactive or stale data to low-cost, secure storage.
- Retention Policies: Enforce data retention schedules to meet regulatory requirements like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Risk & Cost Control: Reduce exposure to breaches and avoid unnecessary storage expenses.
By automating these steps, organisations not only meet compliance standards but also ensure that only relevant, high-value data remains in active systems.
3. Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM)
Contracts govern partnerships, procurement, and revenue streams, but manual handling can lead to missed deadlines, compliance risks, and operational delays. CLM automation addresses this by:
- Tracking every stage from drafting and negotiation to approval and renewal.
- Setting automated alerts for key dates, ensuring no opportunities or obligations are overlooked.
- Standardising workflows to maintain consistency across all agreements.
This level of oversight minimises delays, reduces legal risks, and keeps the business relationship lifecycle running smoothly.
4. Customer Lifecycle Automation (LCA)
In customer-facing industries, personalisation and timing are everything. Customer Lifecycle Automation helps businesses:
- Tailor marketing messages based on customer behaviour and lifecycle stage.
- Automate onboarding journeys that engage and educate new users.
- Implement retention campaigns to strengthen loyalty and reduce churn.
Benefits of Automated Lifecycle Management
Lifecycle automation delivers speed with control, the exact balance modern enterprises need to stay compliant, consistent, and ready to scale. By replacing manual handoffs with policy-driven workflows, teams cut busywork, shrink risk, and keep audits clean.
- Eliminates human errors
Automated provisioning, updates, and deprovisioning remove copy-paste mistakes and missed steps, ensuring the right access at the right time every time. - Enforces governance policies
RBAC, least-privilege, SoD, and zero-trust rules are applied consistently across apps and data, turning best practices into always-on guardrails. - Accelerates task execution Routine actions like new-hire setup, role changes, license allocation, and data retention run in seconds, not days, improving time-to-productivity and reducing IT tickets.
- Improves audit-readiness
Built-in logs, attestations, and automated access reviews create clear evidence trails, simplifying audits and helping avoid compliance gaps or penalties.
Net outcome: fewer risks, fewer delays, and fewer surprises with governance embedded directly into everyday operations.
Choosing the Right Automation Tools
The success of lifecycle automation depends on selecting tools that fit seamlessly into your existing identity and IT ecosystem. Look for solutions that:
- Integrate with your identity stack — Compatibility with IAM, IGA, HR, and ITSM systems ensures smooth data flow and avoids information silos.
- Align with security goals — Support for RBAC, least privilege, and zero-trust principles is essential for reducing risk exposure.
- Provide audit-ready reporting — Detailed activity logs and automated access reviews help maintain compliance and pass audits with confidence.
- Scale with your business — Choose platforms that can handle growth in users, applications, and compliance requirements without adding complexity.
TechPrescient’s unified lifecycle automation platform delivers on all these fronts, offering seamless integration with diverse identity infrastructures while ensuring governance, compliance, and operational efficiency remain uncompromised.
Real-World Examples of Lifecycle Automation
Lifecycle automation isn’t theoretical—it’s already transforming operations across industries:
- Financial Services — Automating identity lifecycle processes ensures immediate deprovisioning of terminated staff, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive financial data and reducing insider threats.
- Healthcare — Data lifecycle automation archives inactive patient records and enforces HIPAA-compliant retention schedules, protecting privacy while optimizing storage.
- SaaS Providers — Customer lifecycle automation personalizes onboarding workflows, boosting adoption rates and reducing churn in competitive subscription markets.
- Large Enterprises — Application lifecycle automation speeds up DevOps pipelines by automating testing, integration, and deployment—accelerating time to market without sacrificing quality.
- Legal and Procurement — Contract lifecycle automation tracks agreements from drafting to renewal, eliminating missed deadlines and minimizing manual oversight.
These examples show how automation removes friction, strengthens compliance, and delivers measurable business value no matter the industry.
- Discover how unified lifecycle automation can improve efficiency, strengthen compliance, and reduce risk.
- Book a personalized demo to see how our platform fits into your environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What’s the difference between ALM and ILM?
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) focuses on managing the lifecycle of software applications from development and testing to deployment and retirement. Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM) manages the lifecycle of user identities, including onboarding, role changes, access reviews, and offboarding. Both rely on automation but serve different domains: ALM streamlines software delivery, while ILM secures and governs access to systems and data.2. Why is lifecycle automation important for cybersecurity?
Automating lifecycle processes ensures that access provisioning and deprovisioning happen securely and on time, eliminating delays that leave systems exposed. It also enforces governance policies, prevents privilege creep, and reduces attack surfaces created by orphaned accounts or outdated permissions.3. Which tools support automated lifecycle management?
There are multiple tools depending on the domain. For ILM, platforms like SailPoint or Okta are common. For ALM, tools such as Azure DevOps or Jenkins are widely used. Informatica supports Data Lifecycle Management (DLM), and Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM) platforms like Icertis automate contract workflows.4. Is lifecycle automation only for large enterprises?
No. Mid-sized businesses also benefit significantly from lifecycle automation. It reduces IT workload, improves security, speeds up processes, and ensures compliance—without requiring the large budgets or teams often associated with enterprise IT.5. Can lifecycle automation integrate with HR and IT systems?
Yes. Modern lifecycle automation platforms provide APIs, SCIM support, and ready-made connectors to integrate with HR systems like Workday or SAP SuccessFactors and IT systems like ServiceNow or Active Directory, enabling seamless, end-to-end automation.