What is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?


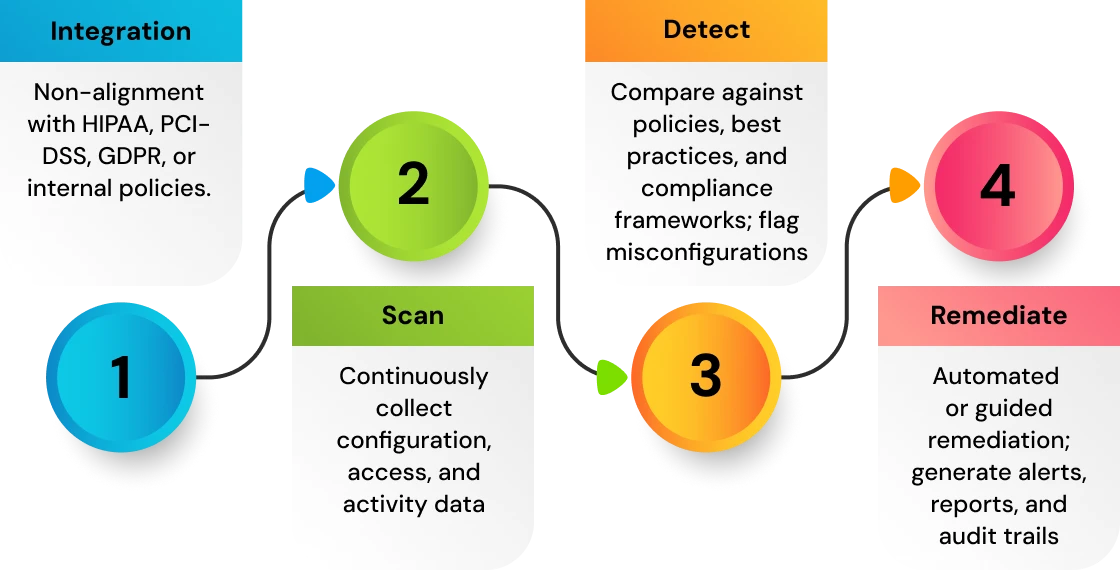
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) refers to the process of identifying, monitoring, and remedying risks in a cloud infrastructure. CSPM tools automate the detection of misconfigurations, policy violations, and compliance gaps of any of the services offered in IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. CSPM effectively assesses an organisation's cloud resources continuously, such as its storage buckets, virtual machines, and APIs, which assists organisations with managing the risks of cloud breaches and maintaining best security practices, as well as compliance with relevant regulations or maps, if applicable. CSPM can help organisations utilise single-cloud, hybrid cloud, or multicloud environments. With many organisations moving into hybrid and multi-cloud architectures, the complexity of configuration drift and visibility gaps makes it less practical to rely on oversight. In fact, misconfigured cloud systems are a contributing factor in over 23% of cloud security incidents, ranking among the top causes of cloud breach events.
In today’s cloud-first and fast-paced reality, the security challenge is no longer “if you’ll be attacked”, but rather “how fast you’ll detect it and contain it.” Cloud Security Posture Management tools remove that hesitation by providing continuous visibility, risk-prioritisation, and automated fixes that allow for cloud security to operate in a proactive manner rather than a reactive manner. In this blog, I’ll share why CSPM is so relevant in modern cloud environments. We’ll look at the key attributes of CSPM, how it works under the hood, compare it to related security tools, look at use cases, benefits and challenges, and finally, I’ll help you consider the right CSPM solution.
Key Takeaways
- CSPM enables automated detection and remediation of configuration errors across cloud environments.
- This minimizes breaches caused by human errors or configuration drift.
- CSPM provides ongoing regulatory compliance, continuous monitoring for alignment with regulatory frameworks.
- CSPM fits within DevSecOps workflows and integrates security seamlessly into cloud development.
- By utilizing a CSPM, you are a few steps closer to real-time visibility, context, and automated remediation.
Why Is CSPM Critical in Modern Cloud Environments?
As organizations increasingly transfer workloads to the cloud, the operational complexity of managing configurations, access controls, and compliance obligations increases exponentially. Misconfigurations, excessive permissions, and inconsistent policies are now the primary drivers of cloud security incidents. According to Gartner, through 2025, 99% of cloud security failures will be the customer's fault, and 90% of organizations that fail to maintain control over their use of public cloud will fail to share sensitive data appropriately. These statistics suggest that in cloud environments, the most risk does not stem from the cloud itself, but from the management of the cloud.
Hybrid and multi-cloud deployments further increase complexity by multiplying the services, APIs, and configurations that require monitoring. Continuous visibility into cloud usage cannot be achieved through manual audits or static policy enforcement alone. Without a centralized view and ongoing assurance that controls are applied, organisations are likely to overlook misconfigurations or other security gaps.
-
Misconfigurations:
Misconfigurations are responsible for most breaches of cloud security. Common examples are public storage buckets, users with excessive IAM roles, insecure APIs or left default security settings unchanged. One example is that a misconfigured AWS S3 bucket can expose sensitive customer data, which has happened in many breaches. Additionally, an expansive use of “admin” role privileges throughout cloud workloads means an attacker can quickly escalate privileges after they gain access to a set of valid credentials. -
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Complexity:
Modern enterprises are deploying workloads across multiple providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) and in conjunction with SaaS applications. Each provider implements its controls, settings, and compliance frameworks. Without a centralized view of workloads, security teams can lose visibility significantly concerning asset tracking, privileges or configurations pertaining to the security baseline. For example, a security team may successfully implement network rules in AWS and miss the equivalent controls in Azure or vice versa, which is another point of vulnerability that an attacker can easily exploit.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools help mitigate these risks by providing:
- Continuous visibility: Providing real-time mapping of assets across AWS, Azure, GCP, and SaaS.
- Automated monitoring and remediation: Identifying drift from security baselines and automatically remediating risky configurations.
- Compliance enforcement: Ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR, and ISO 27001.

Key Features of CSPM Tools
Modern Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions do more than monitor cloud resources. In addition to providing automated remediation, they provide continuous compliance monitoring and risk prioritization, allowing security teams to demonstrate proactive detection and remediation against any misconfigurations before a breach occurs. CSPM tools help organizations comply with regulations with less human error and work across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, reducing manual labour and simplifying security operations.
1. Automated Discovery and Asset Visibility
One of the key features of CSPM solutions is the ability to continuously scan cloud environments and generate a real-time inventory of cloud resources. This inventory encompasses all cloud resources, including virtual machines, storage, databases, and SaaS applications. Security teams receive a unified level of visibility across their cloud service providers, including AWS, Azure, GCP, and any third-party PaaS or SaaS applications, using easily navigable dashboards. The simultaneous visibility of your assets across all cloud environments will allow you to easily identify any unexplored shadow IT and unmanaged resources in your infrastructure.
2. Continuous Configuration Monitoring
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) platforms can monitor your cloud resources against established security baselines to look for configuration drift, misapplied policies, or deviations from best practices. Scans can be run across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS environments, so even minor changes can be flagged, added to a queue, and remediated if they will introduce risk.
3. Risk Prioritization and Context
Not all misconfigured resources have the same level of risk. CSPM tools provide contextual-aware prioritization to evaluate the risk of certain vulnerabilities, in terms of possible impact and potential attack paths. Alerts can also be intelligently filtered so you are not overwhelmed by alerts, and work can be focused on more pressing issues that might expose content or violate compliance.
4. Compliance Reporting and Auditing
CSPM services support compliance with standards such as CIS, NIST, GDPR, and HIPAA. They create audit logs, compliance dashboards, and report generation in real-time so that internal or external audits become easier. By having continuous adherence to regulations in place, they eliminate manual interaction for compliance.
5. Automated Remediation
Automated remediation is offered by most CSPM solutions so that a pipeline can fix a misconfiguration at the time of the error, for example, an S3 bucket that is not secured or an IAM role that is overly permissive. CSPM options can also be integrated into a DevOps pipeline, so that continuous security practices are met in conjunction with CI/CD flows and a misconfiguration is addressed prior to pushing code to production.
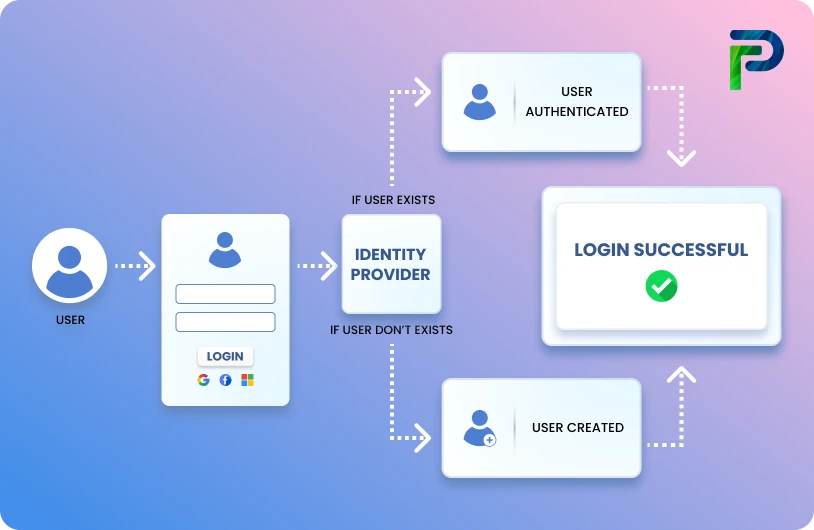
How CSPM Tools Work?
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions connect directly into cloud environments through agentless, API-based integration. This direct connection allows organizations to continuously monitor and remediate risk across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS without the overhead of installing agents or proxies. When a CSPM tool is connected to a cloud environment, it provides a cycle of visibility, detection, contextual risk analysis, and remediation, allowing enterprises to secure public cloud and multi-cloud environments at scale.
-
Connect to your Cloud Environments
CSPM solutions integrate directly with cloud provider APIs, enabling an agentless architecture. Organizations provide either read-only access (to just see what's there) or limited read/write permissions (to allow for automated remediation). Nearly all providers support AWS, Azure, and GCP, with many offering support for Oracle, Alibaba, and IBM Cloud as well. A flexible integration of this sort makes visibility faster and easier across hybrid and multi-cloud ecosystems, all without impacting applicability workloads. -
Gain Visibility
Once connected, the CSPM tool will dynamically inventory all cloud asset types, including all instances, storage accounts, containers, and serverless functions and then capture configurations, audit trails, network traffic, and cloud events. This gives teams a unified view of their cloud footprint by serving up all of the information in one place, eliminating a lot of the blind spots that exist from manual cloud monitoring or security tools that run in silos. -
Identify Misconfigurations and Compliance Violations
CSPM comes with hundreds of pre-built policies mapped to industry frameworks (e.g., CIS Benchmarks, NIST, PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR). These policies continuously evaluate resources for issues like:
- Amazon EC2 instance with IMDSv2 disabled
- Azure Kubernetes Service endpoint is publicly accessible
- GCP API keys have not been rotated within 90 days
Any violation is flagged, providing security teams with immediate insight into misconfigurations that could lead to breaches or compliance failures.
-
Detect Threats in Real-Time
Unlike traditional security-related approaches, which rely on proxies or agents on endpoints, CSPM approaches leverage cloud-native telemetry (for instance, AWS CloudTrail logs, Amazon VPC flow logs, and Azure activity logs) to identify anomalies. Many solutions offer threat detection based on AI/ML software and User & Entity Behaviour Analytics (UEBA), and they map suspicious activity to known threat frameworks (e.g., MITRE ATT&CK). This capability helps teams detect threats such as unauthorised access attempts, privilege escalation, or potential data exfiltration without additional infrastructure overhead. -
Contextualize Risks with Graph-Based Analysis
Organizations typically find themselves with thousands of misconfigurations. Instead of simply generating alerts, a CSPM tool evaluates risk based on context, data sensitivity, internet exposure, privilege, and threats actively targeting their organization. Many CSPM solutions use graph databases to create maps of asset relationships and attack paths (e.g., a misconfigured IAM role + exposed storage bucket + overly permissive network rule). This helps teams understand how individual issues combine into real-world risks, improving remediation focus. -
Remediating Issues
CSPM solutions support remediation in multiple ways:
- Providing step-by-step manual remediation instructions (which can encourage collaboration with developers).
- Integration with security information and event management (SIEM), security orchestration automation and response (SOAR), IT service management (ITSM), and collaborative tools (e.g., ServiceNow, Jira, Slack) for workflow automation.
- Automated remediation through the CSPM console for certain risks (e.g., closing opened S3 buckets, enforcing encryption, and revoking excess IAM permissions).
This blend of manual and automated processes allows for faster response times while still providing organizations with oversight of any risk remediation.
- Monitor Trends and Report Compliance
CSPM tools don't merely remedy incidents; they constantly observe environments and fulfil a trend analysis role to demonstrate if overall risk is trending downward. Some have built-in reporting capabilities to enable security teams to demonstrate their compliance posture in a clear, concise manner, including:
- Percentage of compliant resources across frameworks.
- Passing/failing controls against PCI DSS or HIPAA.
- Detailed, audit-ready PDF/CSV reports for regulators and stakeholders.
Compliance reports help security leaders track improvement, demonstrate value and communicate effectively to business executives, as well as prepare for external audits.
CSPM vs Other Cloud Security Solutions
Although CSPM is important for detecting misconfigurations and maintaining compliance, it isn't used in isolation. Organizations generally utilize CSPM in conjunction with other solutions like CNAPP, CWPP, CIEM and SIEM to achieve full coverage across cloud security. The table below highlights key differences and integrations of these solutions.
| Feature | CSPM | CNAPP (Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform) | CWPP (Cloud Workload Protection Platform) | CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management) | SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Focus | Identifies misconfigurations, compliance gaps, and visibility issues in cloud environments. | Provides end-to-end protection for cloud-native applications, integrating CSPM + CWPP capabilities. | Protects workloads (VMs, containers, serverless) at runtime against malware, exploits, and vulnerabilities. | Manages and governs cloud entitlements, minimizing risks from excessive or unused permissions. | Collects, aggregates, and analyses logs for threat detection and incident response. |
| Use Case | Posture visibility and compliance assurance across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. | Unified platform for application security, combining posture management, workload protection, and pipeline scanning. | Secures workloads at runtime, detects anomalies, and prevents lateral movement. | Enforces least-privilege policies by detecting over-permissioned accounts, roles, and identities. | Provides centralized monitoring and forensics by correlating logs across cloud and on-prem systems. |
| Scope | Focuses on configuration state and policy enforcement. | Broad scope: includes misconfigurations, runtime protection, vulnerability scanning, and IaC security. | Limited to workload-layer protection, not configuration or entitlement issues. | Narrow scope: specializes in managing identity/entitlement risk in cloud environments. | Very broad scope, but primarily retrospective (detects after events occur). |
| Strengths | Continuous visibility, automated remediation, and compliance reporting. | Holistic cloud-native security reduces tool sprawl. | Runtime protection against active threats. | Fine-grained identity and access governance. | Strong incident response and threat hunting capabilities. |
| Limitations | Doesn’t provide runtime workload protection or deep entitlement management. | Complex and may be overkill if only misconfigurations are a concern. | Cannot detect misconfigurations or compliance violations. | Lacks visibility into broader cloud posture beyond access. | Not purpose-built for cloud misconfigurations or entitlement risks. |
| How They Complement CSPM | — | Builds on CSPM to create unified cloud-native protection. | Works with CSPM by securing workloads once posture is hardened. | Adds depth to CSPM by focusing on identity risks and access controls. | Enhances CSPM by providing log-based detection, investigation, and compliance reporting. |
Who Needs CSPM? Use Cases Across Industries
Cloud Security Posture Management is no longer just a “good to have.” It has evolved into something that organizations in regulated industries, where sensitive data is being managed, or if you have a large-scale cloud environment, need to have. Detecting misconfigurations, enforcing compliance, and remediating issues in near real-time gives CSPM value in the following instances:
-
Finance: Securing Data and Meeting SOX/PCI-DSS
Financial institutions are entrusted with a high volume of sensitive customer data and transactional data. One misconfigured database or storage bucket can expose millions of records of sensitive data. CSPM helps organisations enforce compliance with frameworks such as SOX and PCI-DSS, ensure the proper encryption standards are met, and automate reporting to the regulators. Organisations need to reduce the chance of misconfiguration risks to ensure the bank or fintech does not experience a data breach that impacts customer trust in the organisation and/or triggers penalties. -
Healthcare: HIPAA Compliance and Access Reviews
By their very nature, healthcare providers, and more critically, insurers, are required to meet strict regulations under the goals of HIPAA to keep patient health information secure. In a cloud environment, CSPM can be used for continuous monitoring of access controls, identity privilege review, and data storage configurations. Automated alerts for unauthorized changes and periodic access reviews will ensure that PHI is always secure for compliance and patient trust. -
SaaS: Oversight of Cloud-Native Arrangements at Scale
SaaS vendors frequently function across multi-cloud infrastructures to deliver a global customer base. CSPM operates at scale and continuously scans for misconfigurations, excessive permissions, and insecure APIs. With automated compliance mapping, SaaS organizations can quickly evidence compliance over global regulations, decreasing the risk of downtime for themselves and sustaining the uptime and trust that their customer expect. -
Enterprise: Centralized Governance Across Providers
Corporations operate workloads across AWS, Azure, and GCP, and alongside SaaS. Without CSPM, governance has multiple places, and visibility is lost. CSPM provides a single pane for assets, enforces a consistent security baseline, and simplifies business unit reporting. The centralized governance mitigates audit fatigue and ensures misconfigurations will be detected no matter where workloads are running.
Benefits of Cloud Security Posture Management
CSPM solutions are not simply viewed as extra tools; they result in measurable improvements in security posture, reduction in risk exposure, and ROI. CSPM enhances security by automating tedious security checks, providing visibility of the state of security in real time, and reinforcing compliance with various compliance frameworks, all while enabling you to safeguard sensitive data and save time and money.
1. Fast Remediation via Automation
Cloud security traditionally relies on manual audits performed periodically. Unfortunately, this can result in vulnerabilities remaining unaddressed for weeks or even months. CSPM tools continuously assess cloud configuration, and when a misconfiguration is detected, they will automatically trigger a remediation workflow, for instance, closing a vendor’s exposed storage bucket or revoking excessive privileges to a user. CSPM can reduce remediation times from weeks to hours, ultimately mitigating risk to your organization by reducing the time window for an attacker to exploit a misconfiguration.
2. Cost Savings via Breach Prevention
Recovering from a cloud breach is costly, and can include direct incident response costs, fines from regulatory oversight, and long-term impacts to brand reputation. According to a new survey from IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, the average cost of a data breach is $4.4 million worldwide. By demonstrating actionable insight into cloud misconfigurations and fixing them promptly, CSPM will help mitigate the risk of a breach occurring, along with the associated expense.
3. Improved Collaboration with DevSecOps Workflows
In cloud-native environments, security should never be an afterthought. CSPM integrates directly into the DevSecOps pipeline, allowing developers, operations teams, and security to work together without any friction. Policy checks are automated into Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) templates for secure configurations prior to deployments. This enhances collaboration between teams, improves development cycle speed, and starts security in workflows rather than adding it later.
Challenges and Considerations
Although CSPM platforms provide a great deal of value, there are many challenges to overcome in their adoption. Security leaders need to consider complexity in tools, organizational readiness, and integration challenges to ensure successful implementation and use over time.
1. High Alert Volume can Lead to Overwhelm for your Team
The most common challenge with CSPM tools is the number of alerts they generate. If you do not properly tune the alerts, your teams may find themselves with thousands of alerts each day, many of them minor alerts or duplicates. This leads to "alert fatigue", and it is easy for the more critical issues to be missed. Organizations should consider adopting risk-based alerting, grouping some of their findings by severity and potential attack path relevance.
2. Must Integrate with Existing Cloud-Native and DevOps Tools
To maximize value from your CSPM, it needs to integrate with your existing workflows. Most organizations use a mix of cloud-native security controls, SIEMs, CI/CD pipelines, and Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) frameworks. Without proper integrations, visibility becomes siloed, and efforts can become duplicated. Choosing a CSPM solution that uses APIs or connectors for your findings greatly improves the usability and actionability of your findings in a DevOps pipeline or a SOC workflow.
3. Different Levels of Maturity Across Providers
The CSPM landscape has changed quickly, and providers do not all have as mature solutions. Traditional vendors may only give users basic visibility or compliance, while more modern solutions incorporate risk prioritization, automated remediation, and threat intelligence. Organizations should take the time to assess the maturity of their vendor and appropriately align tool capabilities based on cloud complexity and security maturity.
Choosing the Right CSPM Solution
Cloud Security Posture Management platforms vary considerably in quality and features. With dozens of vendors in the marketplace, organizations need to assess which solution is appropriate for their cloud complexity, compliance, and operational maturity. Optimal solutions should do more than just static monitoring and provide real-time visibility, contextual risk information, and integration into existing workflows.
1. Look for Agentless Architecture
Agent-based deployments can slow down your adoption and add operational overhead. Modern CSPM solutions use agentless APIs to connect directly with cloud providers, allowing for fast setup and monitoring in real time without needing to install additional software on workloads. These types of solutions reduce needless friction for DevOps teams and time-to-value.
2. Evaluate Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Support
Most larger enterprises have at least one provider. For example, using AWS for core workloads, Azure for enterprise applications, and GCP for AI/ML. A solid CSPM platform must present unified visibility across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, implementing policies and monitoring configurations for all providers in one tool.
3. Audit AI and Automation Capabilities
As cloud environments grow, manual investigation and remediation are impractical for security teams. Choose a supported CSPM vendor that utilises augmented AI, risk prioritization, which will expose and highlight the risks from misconfigurations that put you at the greatest risk. Also, CSPM should include some level of automation to auto-remediate any potential issues, such as open storage buckets or over-permissioned IAM roles. Allowing for periodic evaluation of security issues, while decreasing alert fatigue and calculating mean time to remediation (MTTR).
4. Evaluate CNAPP Product Strategy
CSPM is evolving and trending into Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms, CNAPPs are an integration of the best products in the CSPM, CWPP - Workload Protection, as well as CIEM - Cloud Identity Enterprise Management. Understanding a vendor’s product strategy will help you understand long-term scalability as well as future-proofing your investment so that organizations can finally start to progress to more holistic cloud security without having to rip and replace all of your current vendors.
Final Thoughts
Cloud Security Posture Management is now an essential facilitator of proactive cloud security. In hybrid and multi-cloud environments where workloads and data are dispersed, the conventional perimeter barriers no longer work. CSPM continuously assesses configurations, identifies drift, and remediates serious issues, freeing security teams from reactive firefighting to proactive risk management activities.
With visual contextual awareness and automated compliance, organizations can make intelligent prioritization of threats, protect sensitive data, and minimize risk of exposure to misconfigurations. CSPM drives teams to make informed, real-time decisions that transform intricate cloud spaces into secure, resilient, manageable infrastructure.
NEXT STEPS
Strengthening cybersecurity posture requires the right mix of strategy, automation, and continuous oversight. With Tech Prescient’s Identity Confluence, you can gain the visibility and control needed to reduce risk and stay audit-ready.
- Get started faster → Explore now
- See it in action.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a CSPM tool?
A Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tool permits continuous assessments of your cloud environments for misconfigurations, excessive permissions, or compliance gaps across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. CSPM tools not only monitor for those risks, but they also offer remediation processes and reports to help keep your cloud resources secure.2. How does CSPM help with compliance?
CSPM scans your cloud configuration against regulatory compliance frameworks, such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and CIS benchmarks. It performs real-time checks against these frameworks, builds compliance reports, and provides audit logging for your cloud environment, which equalises compliance requirements and greatly reduces the amount of resource hours spent on compliance activity.3. Can CSPM prevent data breaches?
No tool can ever remove all risk, but CSPM definitely decreases the likelihood of data breaches that may occur from misconfigurations or policy violations. CSPM tools identify vulnerabilities in your cloud environment and automatically remediate high-risk issues with little to no user intervention, acting as a proactive measure when it comes to sensitive cloud workloads.4. What's the difference between CSPM and CNAPP?
CSPM is a specific part of a Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP). CSPM gives you functionality specifically focused on the detection of misconfiguration, compliance, and posture management. The CNAPP is a worldwide integrated solution for CWPP (workload protection), CIEM (identity and access governance), and full-stack cloud security monitoring.5. Is CSPM necessary for single-cloud environments?
Yes. Even organizations using a single cloud provider can benefit from CSPM. CSPM provides continuous visibility and compliance, detects misconfigurations, and enforces security policies, which all contribute to safer and more effective cloud operations.