Modern RBAC - The Future of Role-Based Access Control


Traditional role-based access control (RBAC) systems are showing their weaknesses in most organizations today. Static hierarchies, inflexible roles, and continual manual certifications produce an explosion of roles where managing thousands of overlapping roles becomes unmanageable. As a result, IT and security teams spend more time ensuring access than managing and improving access.
Modern Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) intelligently adapts. It leverages traditional RBAC concepts while adding contextually aligned policies, business roles and application roles to make access work in terms of real business context. With AI-based role mining, modern RBAC supports ongoing optimization and delivery of least privilege at scale, without constant manual effort.
This blog will outline what modern RBAC is, how it differs from traditional models and why modern RBAC is an imperative in organizations with a focus on agility, compliance, and efficiency of identity governance.
Key Takeaways
- Modern RBAC introduces agility and scalability to access governance with dynamic, policy-driven control.
- Business and application roles make access design, assignment, and review much simpler.
- AI and automation continuously optimize roles, reducing role sprawl and manual work.
- Modern RBAC supports more compliance and least-privilege enforcement across the organization.
What is Modern RBAC and Why Does It Matter?
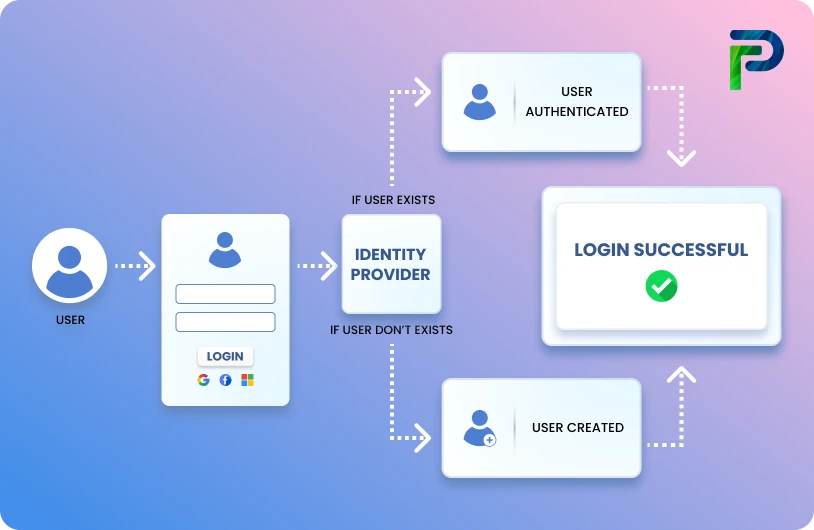
Modern Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is an upgraded iteration of traditional RBAC tailored for the demands of modern, agile IT environments. Instead of being static and requiring manual upkeep, now through automation, policy-based controls, and contextual intelligence, access management can become dynamic and more accurate without sacrificing scale or business alignment.
Access management is steered by business context and policy in modern RBAC rather than merely who the user is (like the job title or department). This means determining who the user is, what the user needs to do, and in what context access should be allowed.
For example, rather than manually assigning multiple permissions to each employee in a department, you would establish a business role such as "Sales Manager." This business role can then dynamically provision the appropriate applications, roles, and entitlements based on yet-to-be reflected or preconfigured rules and the user's responsibilities.
This method not only simplifies administration and diminishes the chance for excessive permissions, but it also guarantees that access decisions keep pace automatically with shifts in users or business needs.
Why does it matter?
This method allows organizations to enforce the principle of least privilege at scale, which means users have only the access they absolutely require, and it makes it easier to pivot when roles, teams, and/or technologies change. It also works seamlessly with AI and role mining tools that constantly look at patterns in access data to promote new roles that are optimized or flag roles that are needed or that are outdated.
Modern RBAC matters because it allows organisations to go from a reactive to a proactive identity governance approach. It lightens the administrative burden of manual provisioning, it enhances compliance based on policies being enforced, and it provides a single, business-facing framework for access management across cloud, hybrid and on-prem environments.
Overall, modern RBAC converts access governance from a static checklist into a living governance framework, evolving as your organisation evolves without losing either security or agility.
Modern RBAC vs Traditional RBAC: Key Differences
Although traditional RBAC models established the basis for access control, they tend to be inflexible, driven by IT, and are susceptible to role explosion as organizations grow. Modern RBAC, however, is largely able to overcome these limitations with the introduction of dynamic, policy-based frameworks that allow access to be based on organization needs, automate role management, and provide structured governance to ensure compliance. The table below illustrates the major differences between traditional and modern RBAC:
| Aspect | Traditional RBAC | Modern RBAC |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Based on a user's predefined, fixed role (e.g., Sales Manager, IT Admin). | Based on a combination of a user's role and dynamic attributes, such as department, location, device, and time of access. |
| Role Management | Roles are manually created and updated by IT administrators. | Role creation and optimization are automated using AI and analytics. |
| Scalability | Scaling is limited and often results in role explosion. | Modern RBAC scales efficiently by mapping business and application roles. |
| Access Context | Access is assigned solely based on static job titles or functions. | Access decisions are context-aware, considering function, location, device, and risk level. |
| Policy Enforcement | Policies are minimal and often enforced manually. | Policies, including segregation of duties (SoD) rules, are enforced automatically. |
| Certifications | Access certifications are manual and repetitive. | Certifications are streamlined, focusing only on exceptions with intelligent recommendations. |
| Business Alignment | Access control is IT-centric and not closely aligned with business objectives. | Access is aligned with business roles, ensuring clarity and compliance. |
| Maintenance Effort | Requires high administrative effort for ongoing role updates. | Automation reduces manual workload and simplifies maintenance. |
| Adaptability | The model is rigid and slow to adapt to organizational or system changes. | Modern RBAC is adaptive and evolves with the organization’s changing needs. |
| Best For | Organizations with well-defined, static roles and straightforward access needs. | Large, complex, or highly regulated organizations that require adaptive, context-sensitive access decisions. |
| Example | Assigning “Finance Manager” role with a fixed set of permissions across all systems. | Assigning a “Sales Manager” role dynamically based on department, location, and device risk score. |
How Policies, Business Roles, and Application Roles Enable Modern RBAC
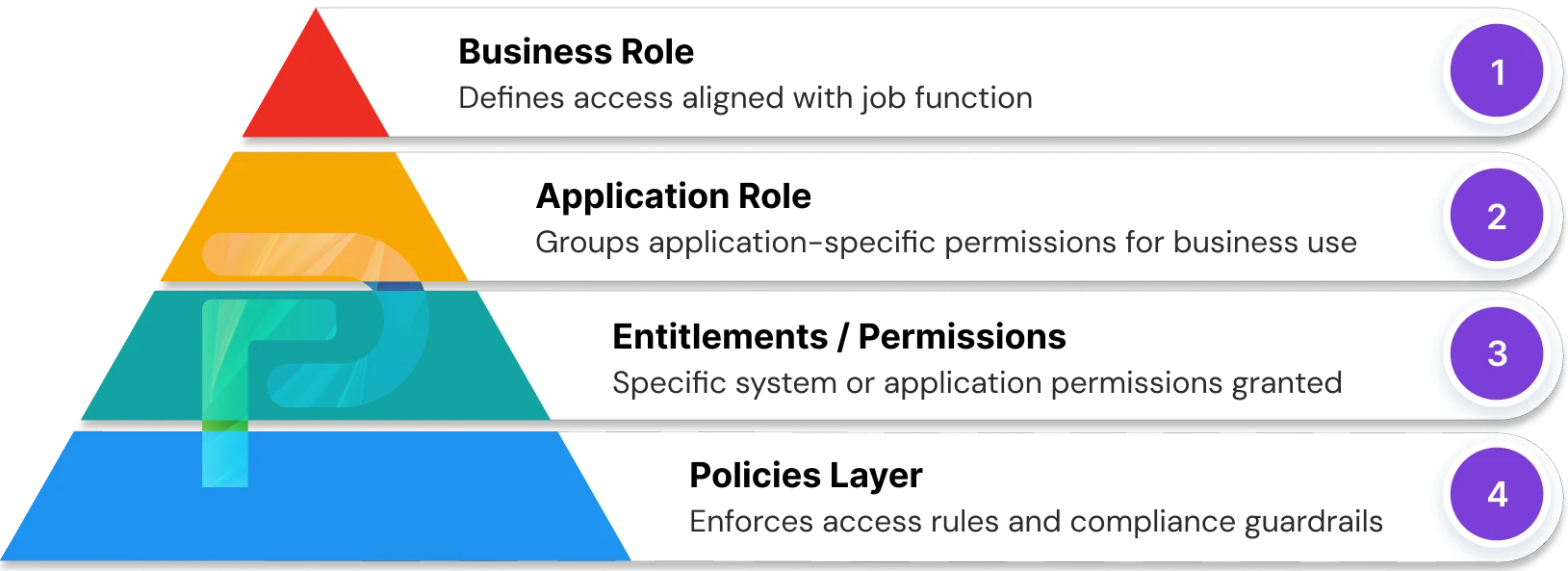
Modern role-based access control (RBAC) is successful because it is organized around access in a way that reflects business functions while also enforcing security and compliance policies. At the heart of RBAC are three areas - policies, business roles, and application roles - that work together to support a scalable, auditable, least-privilege access model.
-
Policies
Policies in RBAC serve as the parameters for all access. They enforce segregation of duties (SoD) and avoid permission conflict or “toxic combinations.” RBAC policies ensure that all access is compliant with regulatory and organizational requirements. By defining what is allowed, prohibited, or requires additional approval, they also create uniform governance in the enterprise. -
Business Roles
Business Roles (BRs) refer to the job function or responsibilities a user has within the organization. By determining the scope of access for the roles, organizations can aggregate human work into access profiles that align with real business needs. For instance, the Financial Analyst role would automatically include access to reporting tools and accounting applications without providing excessive privileges beyond their business function. -
Application Roles
Application Roles (ARs) stipulate the tasks a user can engage in an application. Instead of assigning discrete permissions, you group related privileges together, like “read,” “write,” or “admin,” that govern the specified actions into workable sets that can be managed and implemented easily.
Here’s how it works:
- Developers define roles: The application’s developer is responsible for creating the roles in the system (for example Microsoft Entra ID or in the application itself).
- Administrators assign roles: Admins assign the roles at a later date corresponding to user responsibilities. For example, HR staff may be granted access to view their employees’ information, while IT administrators are allowed to make configuration changes to the system.
- Roles are included in tokens: When a user logs in, the user’s security token will identify the assigned application role.
- Applications enforce access: The application receives the user’s token and knows the permissions that the user is allowed, only allowing access to the options connected with that particular role.
Using application roles allows organizations to control access in a more efficient manner, to reduce manual effort in account management, and to confirm all privileges are appropriate to the user’s job function without unintended privileges.
The Role of AI and Role Mining in Modern RBAC
As companies expand, the task of manually analyzing access patterns and optimizing roles becomes more and more complicated and prone to error. Role mining and AI-powered RBAC are essential elements of a contemporary RBAC model that automate process and enhance identity governance.
-
Role Mining
Role Mining refers to the analysis of present access data to identify natural groupings of entitlements and to expose unused, duplicate, or conflicting permissions. By analyzing how users are interacting with systems and applications, role mining finds opportunities to consolidate roles, mitigate role explosion, and create access that meets business needs. Role mining also finds violations of segregation-of-duties policies and brings attention to orphan or stale accounts. -
AI-driven RBAC
AI-Driven RBAC expands on role mining through the continuous oversight of role patterns using machine learning algorithms and automated recommendations for new or modified roles for the business and applications. Tools can determine the need for a role based on the addition of a new job function, recommend a new job for an anomalous request to access an application, and even simulate scenarios to test the impact of changes before they are made. Most critically, it enables consistent ongoing least-privilege access, supporting compliance, and consistent adaptation to changes in a fluid organization.
Every organization needs to use both tools to their utmost to minimize administrative time, increase accuracy, create a living, dynamic role-based access model that scales more easily, and provide systemic security and compliance across the organization.
Benefits of Modern RBAC for Organizations
Modern Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) fundamentally changes how organizations manage access by integrating automation, policy enforcement, and intelligence. Rather than relying on static role models of the past, it introduces agility, accuracy, and control for the organization. Here are the key benefits modern RBAC brings:
1. Compliance Readiness
Modern RBAC enforces segregation of duties (SoD) policies automatically and enables the organization to align roles with compliance frameworks such as ISO 27001, SOX, or GDPR. Periodic certifications are enabled through predefined policies and visibility into who has access to what. Whether through dynamic removal of rights using dynamic policy, rights certainty, or attribute-based Role Assignment, all of those who have access and who decided access was justified are easy to trace and audit.
2. Dynamic Least Privilege Enforcement
Instead of static access assignments, modern RBAC means that access can now change dynamically based on roles, policies, and context. This means users, human or otherwise, now only have the minimum permissions to perform their function. Modern RBAC continuously reduces over-permissioning while diminishing the risk of lateral movement.
3. Simplified Audits & Certifications
Auditors can quickly review role assignments and policy enforcement thanks to the transparency provided by modern RBAC systems in documenting access decisions. Automated access reviews and evidence trails speed audit cycles, increase accuracy, and demonstrate compliance with little manual effort required.
4. Scalability through Automation
As organizations grow, managing roles manually becomes impractical. Modern RBAC allows for role assignments, provisioning, and certification cycles to be automated, so enterprise teams can effectively govern thousands of users, applications, and environments in an organization while containing admin workloads.
5. Continuous Optimization through AI
AI-based analytics help organizations benchmark roles, unused entitlements, and new access patterns. This creates a feedback loop for organizations to revise roles and policies over time as business structures and threat environments change and evolve. This ensures their RBAC model stays aligned with evolving business structures and threat landscapes.
TechPrescient Modern RBAC Approach
At TechPrescient, our modern RBAC framework is built to reconcile the technical complexity with clarity in a business context, and ultimately provide scalable, context-aware and compliant access governance.
-
Application Roles for Meaningful Certifications
In access reviews, managers are often presented with an overwhelming list of technical entitlements with little context to guide them. TechPrescient’s Identity Confluence establishes Application Roles to change this by taking low-level entitlements, grouping them into meaningful business functions, and presenting them in a way that allows the approver to certify access based on what users do, rather than having to decipher technical roles or permission names. -
AI & Automation for Adaptive Governance
We are outlining our roadmap for a suite of governance and compliance features, underpinned by AI, in the areas of role mining and automation-first governance, to review, define, and continually improve role models. AI will analyze real usage data to recommend either new roles or changes to existing roles. This reduces the time and effort that is spent on role design, but allows us to continue fulfilling the least privilege principle. Automation will enforce these changes to roles or create new roles across all our systems to close the governance loop, supporting adaptive governance based on any changes that happen in the organization in real-time. -
Business–IT Collaboration Through Role Mapping
Modern RBAC thrives on collaboration. We will enable shared visibility between business and IT teams by implementing simple role mapping interfaces that draw business roles together to application roles and related entitlements. In this way, every request is transparent, traceable, and created for business needs and to support compliance objectives.
Conclusion
The modern RBAC is the next generation of access governance that replaces static, entitlement-heavy models with automated, dynamic, prescriptive approaches that marry business roles with application roles to provide reliable governance agility, compliance, and visibility into access enterprise-wide.
As identity environments become more dynamic, traditional RBAC may not sustain the pace. Modern RBAC offers a strong, scalable architecture that helps proactively adapt to organizational change, applies least-privilege controls seamlessly, and provides comprehensive governance without losing control. This is not just new access management, it is the beginning of a modern, smarter identity governance approach.
Simplify your governance strategy with Modern RBAC, powered by Identity Confluence
Experience how unified, policy-driven access control streamlines compliance and scales effortlessly across your enterprise.
- Learn more about Identity Confluence → Explore now
- See Identity Confluence in action.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are business roles vs application roles?
Business roles (BRs) define access profiles around job functions, which indicate what an employee should have to perform their job. Application roles (ARs) bundle together technical entitlements within applications into logical groupings that map to business requirements. Through the combination of BRs and ARs, the bridge between business intentions and technical entitlements is established.2. Why are application roles important in identity governance?
Application roles lead to a simplified management of permissions instead of managing each entitlement on its own. Application roles consolidate entitlements into logical groupings, which prevent "role explosion" and assist in access certifications, as well as the least privilege directive. Application roles also allow access to manage entitlements more consistently amongst the applications as they relate to the business function, improving security and audit preparedness.3. How does AI improve role mining in RBAC?
AI-based role mining will review existing access patterns along with user behaviours and identify natural groupings of permissions. These statements will assist companies in improving their roles, detecting redundant/excess access and suggesting new business/application-based roles automatically. All of this will lead to faster and more accurate role maintenance, reduced administrative burden and continual improvements to access governance practices.