What Is the Access Provisioning Lifecycle?

Access provisioning is the process of granting, modifying, and revoking access to an organization’s applications, systems, and data. Its goal is to ensure that every user has only the minimum privileges required to do their job. This includes creating accounts for new hires, issuing credentials, updating access when roles change, and fully revoking access when it’s no longer needed.
As organizations become larger, the number of user identities and user account complexities (implementation of multiple applications) also increases, which creates additional risks. Without a consistent provisioning lifecycle, organizations face challenges with user account "sprawl", orphaned accounts, entitlement creep, and failed audits.
In this blog, we will unpack the access provisioning lifecycle, its stages, the importance of it for security and compliance, common risks, best practices, and how modern IAM and IGA tooling automates and simplifies the whole process.
Key Takeaways
- The access provisioning lifecycle provides a clear framework for granting, changing, and removing user access throughout an enterprise.
- Poorly managed access can lead to entitlement creep, privilege misuse, orphan accounts and failed audits.
- A mature lifecycle can integrate IAM, HR systems, authentication systems, and IGA policies to grant complete visibility and control.
- Automation reduces manual mistakes, improves onboarding speed, and creates consistency in enforcing least-privilege access.
- Strong lifecycle management supports SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and all internal audit needs.
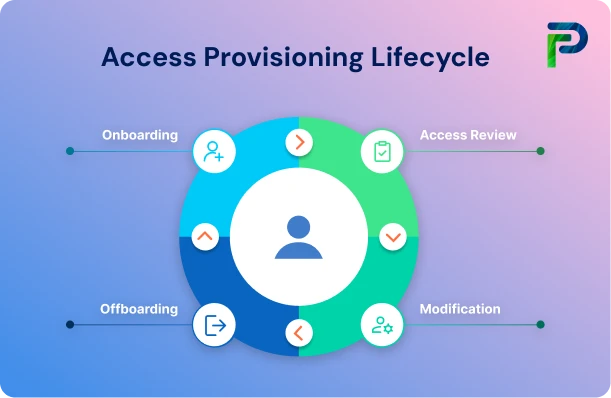
5 Key Stages in the Access Provisioning Lifecycle
Every point in the lifecycle guarantees that users have the right access at the appropriate time and for the right duration. If done correctly, a provisioning lifecycle will have removed unnecessary privileges, improved audit preparedness, and reduced overall identity risk.
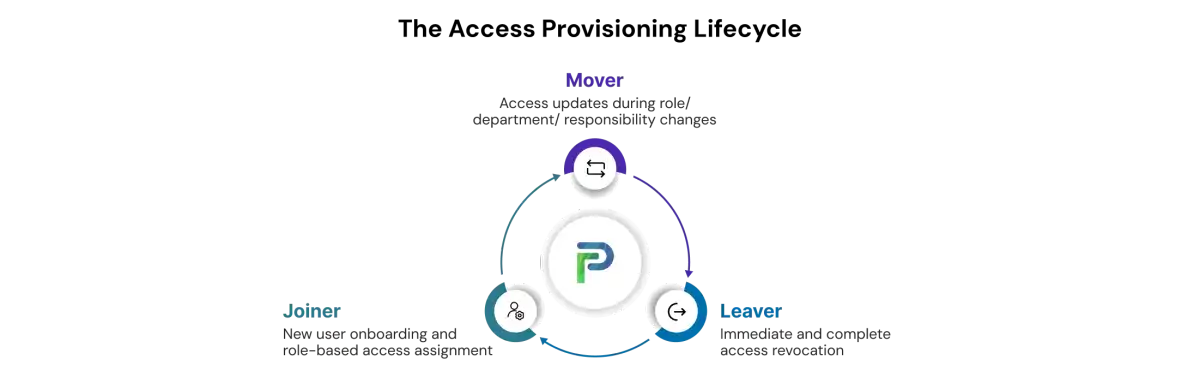
1. Onboarding (Joiner Stage)
The joiner stage starts when HR or a hiring manager begins user record generation in the HRIS. This initiates a digital identity across directories, such as Active Directory, Azure AD (Entra ID), or identity providers. Auto-assigning of credentials, MFA enrollment, and other baseline attributes (department, role, location, manager) happens at this point of identity creation.
- Identity Verification
Before granting any access, the newly created identity must be verified to ensure only legitimate users enter the organization’s environment. Verification may involve passwords, MFA, or biometric checks, depending on security needs.
Once verified, role-based provisioning begins. Users automatically receive access mapped to their job role, applications, groups, shared drives, and cloud resources, without manual tickets. Automated workflows ensure full Day-1 readiness.

2. Access Approval & Provisioning
Once a user’s identity is verified, the next step is to review and approve their access request. Users typically request permissions based on their role or specific tasks. In this stage, you evaluate if the user’s job responsibilities make the request appropriate and align with your organization’s policies and security standards.
Approval paths depend on the sensitivity of the resource—typically involving the user’s manager and, for high-risk apps, the application owner or security team. Policies like RBAC and ABAC determine whether access should be granted, while AI-driven logic helps recommend least-privilege options or flag unusual requests. This stage ensures only necessary, justified access is provisioned, strengthening governance and Zero Trust.
3. Maintenance & Access Review
Once you grant access, you must continuously monitor that access. Over time, permissions unintentionally drift beyond the original intent due to ad-hoc approval processes, unmanaged changes in privilege, or outdated roles. This is commonly called access creep. IAM/IGA systems can help manage this by tracking changes, notifying teams or owners if users become overprivileged, or maintain a privilege that is outside their job requirements.
Organizations will conduct access reviews periodically (quarterly or event-driven) to confirm entitlements still align with job responsibilities. The verification is usually done by managers or application owners, who then can configure report outputs through an IGA tool like Identity Confluence by Tech Prescient that identifies risky permissions, admin rights, stale accounts, or any access that is not being used.
This stage is critical for compliance frameworks like ISO 27001, SOX, and GDPR, where organizations must demonstrate ongoing access governance.
4. Role Change & Modification (Mover Stage)
Users frequently have new responsibilities and/or departments. The change in the roles of users triggers automatic recalibrations to the users’ access (removing access to outdated permissions and issuing a new set of permissions appropriate to their new positions).
HRIS-integrated IAM workflows ensure the change is reflected instantly across all connected systems. It eliminates privilege accumulation, one of the most frequent causes of insider threat and excessive auditor findings.
Automation at the mover stage can also lead to increased productivity: Employees obtain access to the new role on day one, as opposed to waiting for a manually generated resolution process to resolve access issues.
5. Offboarding / Deprovisioning (Leaver Stage)
The final identity lifecycle stage is deprovisioning, where all access is revoked as soon as a user leaves or no longer needs it. The HR termination event should trigger immediate removal of access across directories, cloud/SaaS apps, on-prem systems, VPNs, and any shared resources.
Effective deprovisioning includes disabling accounts, revoking tokens, terminating active sessions, reclaiming licensed software, and rotating passwords for shared or privileged accounts. It also ensures orphaned identities are identified and removed.
Deprovisioning is critical as it prevents former employees or third parties from viewing or misusing sensitive business information and protects your organization’s overall security posture. To support audits, organizations should still retain logs and deprovisioning reports.
Why the Access Provisioning Lifecycle Matters
A good mature access provisioning lifecycle greatly enhances your overall identity security posture. It provides every user with access appropriate to them, for the proper purpose and for the appropriate amount of time, thereby reducing the risk of misuse of privileges and compliance failures. When you use an automated, structured approach to provisioning, security teams can have predictable control over users' identities while enabling users to receive faster access to required resources.
-
Prevents Insider Threat and Data Leakage
An effective access provisioning lifecycle that is properly managed greatly reduces the risks of insider threats and fraud by identifying and removing excessive or obsolete privilege levels before they become a problem. It allows organizations to identify attempts to gain unauthorized privileges, identify unused accounts, and identify inconsistent access patterns that can occur when access is not properly managed. -
Reduces Audit Failures
An effective provisioning lifecycle streamlines your risk of audit failure from a compliance perspective (ISO27001, SOCKS2, SOX-GDPR). Auditor's view of your ability to demonstrate how you build approval processes; as a result of a mature process, Organizations can provide logs to support every decision regarding the granting, reviewing, and revoking of access. -
Improves UX via Automated Access
Additionally, automation greatly enhances user experiences. Users no longer have to wait days to gain access. Managers won’t spend hours reviewing and approving requests. The IT department is freed from the burden of performing repetitive provisioning tasks. This leads to faster onboarding processes, more effective transitions between roles, and an enhanced ability to maintain a safe and secure workspace.

Best Practices for Managing Access Provisioning
Use best practices to develop and maintain a secure, compliant, and scalable Access Provisioning Process that reduces risk, removes manual overhead, and ensures users have the correct level of Access at the correct point in time:
1. Automate Joiner–Mover–Leaver (JML) Events
Automating the onboarding, role change, or offboarding process ensures users have access that corresponds to their employment status. Workflows driven by HR automation will create, update, and delete identities in real time, eliminating waiting times, human error, and orphaned accounts. These automated processes also eliminate the need to manually provision permissions in different systems.
2. Implement RBAC and ABAC Models
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) provides a standardized way of assigning permissions based on job roles. By implementing RBAC, you reduce the likelihood of error when assigning permissions, as well as minimizing potential over-privileged users. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) builds on this by incorporating contextual information about users (e.g. department, location, device trust) to develop a more granular approach to permission assignment based on policy decisions. When RBAC and ABAC are used together, the process produces predictable and scalable Access decisions.
3. Enforce Least Privilege
Users should only be granted the minimum amount of access they need to do their job. By limiting access to the lowest level possible, the risk to the company as a result of an account being compromised is reduced, and any potential exposure to unwanted information is minimized. In addition to users, service accounts, and privileged roles should all adhere to a least privilege methodology and should be reviewed periodically to ensure that privileges have not increased over time.
4. Conduct Quarterly Access Reviews
Regularly certifying access helps to quickly identify unused permissions, misaligned permissions and risky permissions. Quarterly access certifications (for organizations that aren't required to maintain certain compliance standards, more frequently certified access reviews) validate that each user's access relates to their current job responsibilities, and they also highlight where toxic combinations of access exist, where access creep has occurred and accounts that violate separation of duties or SoD.
5. Integrate IAM and IGA for Unified Control
IAM tools manage who is authenticated and manage operational access, while IGA provides the "governance layer" (policies, reviews, SoD controls, audit trail, etc.). When both IAM and IGA are integrated, organizations benefit from a complete and transparent view of who has access to what systems; why that access is necessary; and how and when it should be removed. Both IAM and IGA support compliance and improve security, and are tied closely to the overall governance of an organization.

Common Risks of Poor Access Lifecycle Management
Access provisioning's poor management leads to security weaknesses and compliance risks through unstructured lifecycles of permissions, continued user identities after termination, and decreased visibility within an organization.
1. Access Creep and Privilege Abuse
As users accumulate new permissions due to role changes, they gain excessive permissions compared to what they need. As a result, when an organization's account is compromised, there is a larger number of users with that same account available to attack; therefore, this increases the "blast radius" of a compromised account and makes it easier for insiders to use their power against the organization.
2. Orphaned Accounts Post-Termination
Inactive or abandoned accounts of ex-employees, contractors, or administrators represent a major attack surface that is frequently exploited. If not deprovisioned quickly, attackers can utilize these accounts for covert, ongoing access and bypass standard authentication procedures.
3. Audit Non-Compliance
Auditors look for evidence of changing access, approvals, and provisioning procedures. Whether a company is ISO 27001, SOC 2, or GDPR compliant will depend on how well they manage access to data and who has access to it. If companies do not properly manage the lifecycle of employee access to sensitive data, they risk facing an audit finding, fine, or damage to their reputation.
4. Insider Threats from Excessive Privileges
As the number of accounts with unlimited rights and unnecessary access increases, there is a greater potential for both intentional and unintentional abuse of such access. Unnecessarily elevated privileges, shared accounts, and permissions that allow access without oversight are all opportunities for data to leak and systems to be modified without authorization.
Tools That Automate the Access Provisioning Lifecycle
As previously stated, most current IAM and IGA systems support automating the entire lifecycle of provisioning, fully reducing manual intervention, enforcing policy-based access control, and ensuring continuous compliance.
Most automation solutions include a centralized identity store, which reduces the complexity of approving access requests and ensures continual enforcement of least privilege and a complete audit trail. This is critical to the ability to scale access management across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Key Tool Categories That Enable Access Provisioning Automation
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM) Tools
IAM tools centre on authentication, authorization and operational provisioning.
Core IAM tools provide:
- Automated account creation/updates
- Single Sign-on (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enforcement
- Automated directory synchronisation
- Minimum approval workflows
2. Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) Platforms
IGA tools provide governance, visibility and compliance on top of IAM operational capabilities.
Governance includes:
- Role-based access models and policy-based access models
- Access review and certification workflows
- Separation of Duties (SoD) checklists
- Risk Assessment Scoring and Attestation
- Audit Reporting
3. HRIS-Integrated Provisioning Systems
These tools directly link provisioning and identity lifecycle events with HR tools in order to provide real-time updates.
Capabilities include:
- Automated onboarding/offboarding based on HR events
- Identity attribute synchronisation
- Job Title/Department-based Provisioning
4. Workflow & Access Request Tools
Purpose-Built Tools for managing access requests, approving/rejecting, and assigning tickets for processing.
Attributes of Workflow & Access Request Tools include:
- Self-Service Access Requests
- Multi-level Approvals
- Ticketing System Integration
- Automated Workflows
Identity Confluence by TechPrescient
Identity Confluence offers end-to-end automation for the entire access provisioning lifecycle:
- Real-time joiner/mover/leaver automation
- Policy-based provisioning (RBAC, ABAC)
- Automated access reviews & SoD enforcement
- Full audit trails and compliance reporting
- Connectors for cloud, SaaS, data, and on-prem apps
Ideal for organizations looking to unify provisioning, governance, and compliance under one platform.
Access provisioning tools comparison table:
| Tool Type | Key Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| IAM Platforms | RBAC, automated provisioning, MFA | Okta, Azure AD, JumpCloud |
| IGA Solutions | Access reviews, certifications, workflows | Identity Confluence by Tech Prescient |
| HRIS Integrations | Joiner–mover–leaver triggers | Workday, BambooHR, SAP SuccessFactors |
| Directory Services | Centralized identity, SSO | Active Directory, Google Workspace |
How IGA Solutions Enhance the Access Provisioning Lifecycle
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) is a tool that implements a Governance Layer over the access provisioning processes of traditional IAM (Identity and Access Management) tools by creating a policy-driven approach.
IGA capabilities will enhance how users provision resources through the IGA Audit Control (i.e., identify who is able to authenticate on what), while ensuring that users have the right to authenticate and access what is currently assigned to them, in addition to maintaining compliance with regulations.
Key Ways IGA Enhances the Access Provisioning Lifecycle
1. Policy Enforcement and Attestation
IGA Implementations of role-based, attribute-based, and policy-based access models prevent the inconsistencies/breakdown that occur when users provision ad hoc. All access requests or approvals are reviewed based on established rules (e.g., role catalogues, attribute mapping, segregation of duties policies), and each request includes an attestation for compliance/audit readiness.
2. Segregation of Duties (SoD) Controls
IGA allows for the identification of "Toxic Access Combinations" (i.e. a user is allowed to both create a vendor and approve a payment) before provisioning, which will help to minimise these violations and related risks of financial fraud and non-compliance in an ERP, HR or other key business systems.
3. Centralized Audit Trails and Reporting
The centralized management of audit trails and reports is through identity governance and administration (IGA), which allows organizations to track when, where, and by whom user permission was granted. In addition to logging activities, centralized audit trails provide valuable information regarding policy compliance and approval of permissions.
Logs, certification reports, and compliance dashboards from a centralized location will simplify both internal audits as well as external audits (ISO 27001, SOX, SOC 2, and GDPR), therefore decreasing operational responsibility for IT and Security Teams.
For a deeper breakdown of how governance differs from access management, explore our guide:
IGA vs IAM: What’s the Difference?
Final Thoughts
Identity security relies on an effective access provisioning lifecycle, ensuring identities are created, managed, and removed accurately and on time to reduce risk, close access gaps, and maintain continuous compliance. Organizations adopting an automation-first approach gain consistency across all joiner-mover-leaver events, access reviews, and provisioning workflows. As IAM evolves from manual, operational processes to digitally governed, hands-off IGA, teams establish a single source of truth for identity data and build a stronger security foundation. This unified IAM/IGA strategy enables least privilege, reinforces Zero Trust, and ensures every access decision is intentional, auditable, and policy-aligned.
Unlock automated, compliant, and error-free provisioning.
See how Identity Confluence by TechPrescient transforms your access lifecycle
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the access provisioning lifecycle in IAM?
The Access Provisioning Life Cycle (APL) describes the life cycle of granting, modifying, and terminating user access due to user onboarding, user movement migrated internally, or user offboarding. The APL ensures that each user's identity is granted access based on the user's responsibilities, job functions, and security policies.2. What are the stages of the access provisioning lifecycle?
The APL can be found in many organizations consisting of several distinct stages: Onboarding (a user who is new to the organization), Approval of Access (the process of determining the eligibility of a user requesting access), Provisioning (actual assignment of access to a user), Ongoing Access Reviews (tracking and reviewing ongoing access by each user), and Deprovisioning (terminating access of a user).3. Why is access lifecycle management important?
The importance of implementing an access lifecycle management system within an organization is to help mitigate against unauthorized access to the organization and assist in maintaining an appropriate security posture of the organization. The APL also helps organizations meet compliance requirements as well as eliminates many types of errors associated with manual processes and audit-related gaps.4. How can I automate access provisioning?
By employing IAM or IGA platforms that are integrated with your HR systems and directories. Using these types of automated tools will allow your organization to create user accounts automatically, assign role-based access to the users, modify the users' access to their resources as needed when they change jobs, and remove any access that is to be revoked on the spot when an employee separates from the company.5. What’s the difference between provisioning and deprovisioning?
Provisioning is when you provide a user the ability to access an application, system or resource they need to complete their job duties. De-provisioning is when you eliminate the user's ability to access an application, system, or resource. Typically, you will want to de-provision access during the offboarding process to stop a user from accessing resources when their ability to work at the company has ended.